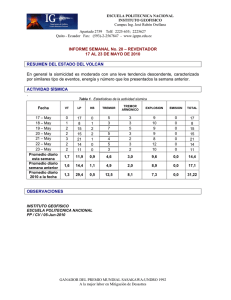
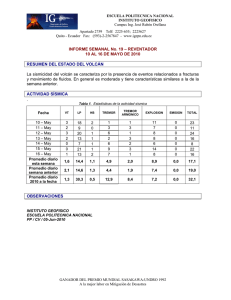
Modales may-might (T)
Anuncio

Modals May y might Usamos may o might para decir que existe una posibilidad sobre algo. o “Where’s Ann?” “She may be at home.” Las formas negativas son may not y might not o mightn’t. o “Where’s Ann?” “She was sick yesterday; she mightn’t come to work today.” Para el pasado utilizamos may have o might have. o “I can’t find my phone” “You may have left it in the book shop.” Could es similar a may o might. o It’s a strange story, but it could be true (it may/might be true). Pero couldn’t tiene un significado diferente a may not o might not. o She couldn’t have got your message (No es posible). o She may not have got your message (No se sabe si lo recibió). Podemos usar may o might para hablar sobre posibles acciones o sucesos del futuro. o Next summer, I may go to England. La diferencia con will radica en que, con este modal existe la seguridad de que ocurrirá lo expresado y, sin embargo, con may o might solo la posibilidad de que suceda. o I’ll be late tomorrow (Seguro). o I might be late tomorrow (Quizá). Podemos usar indistintamente may o might, únicamente utilizaremos might, y no may, cuando la situación no sea real. o If I were Jane, I might buy another car. También existe la forma continua para estos modales: may/might be + gerundio (–ing). Podemos usar esta estructura para hechos futuros o posibles planes. o Don’t come before 8 o’clock, I might be having dinner. o I may be going to England next summer.