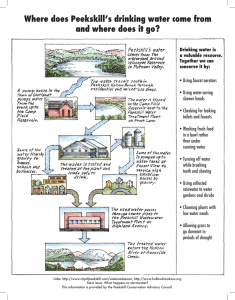
layman`s report
Anuncio

LAYMAN’S REPORT 2012 - 2015 ASSESSMENT AND IMPROVEMENT OF THE URBAN WATER CYCLE ECO-EFFICIENCY USING LCA AND LCC With the contribution of the Life+ financial instrument of the European Commission PROJECT CHARACTERISTICS CARACTERÍSTICAS DEL PROYECTO DURATION January 2012 - May 2015 (41 months) DURACIÓN Enero 2012 - Mayo 2015 (41 meses) BUDGET 1.594.413 € PRESUPUESTO 1.594.413 € Coordinator / Coordinador Stakeholders / Grupos de interés 4-5 02 THE AQUAENVEC PROJECT EL PROYECTO AQUAENVEC 6-7 03 CASE STUDIES: BETANZOS AND CALAFELL CASOS DE ESTUDIO: BETANZOS Y CALAFELL 8-13 04 AQUAENVEC TOOL LA HERRAMIENTA AQUAENVEC 14-15 05 COMMUNICATION ACTIVITIES ACTIVIDADES DE COMUNICACIÓN 16-18 06 OUTCOMES BENEFICIOS Associated beneficiaries / Socios Advisors / Asesores Co-funded by / Cofinanciado por LIFE10 ENV/ES/000520 www.life-aquaenvec.eu 01 CONTEXT AND BACKGROUND CONTEXTO Y ANTECEDENTES 19 04 05 CONTEXT AND BACKGROUND CONTEXTO Y ANTECEDENTES Waste water treatment & discharge Depuración de agua residual y retorno al medio Urban Water Cycle stages Etapas del Ciclo Urbano del Agua Red de saneamiento Distribución de agua potable Urban water activities include water extraction, drinking water treatment, water transport and distribution, sewer network and waste water treatment and discharge. These activities are essential in any urban system to assure reliable supply of drinking water and to ensure water quality when discharging to a water body. Therefore, water management in cities must respond to always more demanding water quality legislations, such as the Priority Substances Directive (Directive 2008/105/EC) regarding drinking water supply or the wastewater treatment directive (Directive 91/271/EEC), both included in the Water Framework Directive (Directive 2000/60/EC). An eco-efficient urban water management assures water supply and wastewater treatment while it limits its environmental impact and minimises the associated costs. Una gestión eco-eficiente del ciclo urbano del agua garantiza el suministro de agua potable y tratamiento de agua residual limitando el impacto ambiental y minimizando costes. Nevertheless, environmental assessment calculators that rose up in previous years are still barely used for decision-making as do not usually integrate economic aspects. When applying these available tools to the urban water cycle management few of them are specific but wide enough to perform an urban water management eco-efficiency assessment. Additionally, life cycle tools require an expert user to decide on goal, scope and impact issues in order to get complex results. Sin embargo, las herramientas para analizar los impactos ambientales disponibles en los últimos años, difícilmente se consideran para tomar decisiones ya que no suelen integrar aspectos económicos. Cuando se han aplicado estas herramientas a la gestión del ciclo urbano del agua, pocas de ellas son lo suficientemente específicas pero flexibles como para integrar un estudio de eco-eficiencia de la gestión urbana del agua. Además, las herramientas de ciclo de vida requieren un usuario experto para decidir el objetivo, alcance e impactos para obtener resultados, a menudo muy complejos de interpretar. Captación y potabilización Water distribution As a part of the urban ecosystem, the urban water cycle management should ensure that drinking water supply and wastewater treatment are performed in a sustainable way reducing their environmental impacts and the associated costs. A pesar de los beneficios obvios del ciclo urbano del agua, raramente se cuantifican ni se asocian los impactos ambientales generados a lo largo del ciclo de vida de los procesos implicados. Por lo tanto, es necesario estudiar la relación entre beneficios y cargas ambientales asociados al ciclo urbano del agua. Water extraction & drinking water treatment Sewer With 80% of European citizens living in urban areas, cities hold a key role in sustainable development. In this context, the Europe 2020 strategy aims at reducing by 20% greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. 01 Despite the obvious benefits of water activities, these are frequently not quantified, and neither are the environmental impacts associated along the life-cycle of all processes involved. Therefore, there is a need to understand the balance between the environmental benefits and the environmental burden associated with the urban water cycle. Con el 80% de ciudadanos europeos viviendo en zonas urbanas, las ciudades tienen un papel clave hacia el desarrollo sostenible. En este contexto, Europa propone una estrategia de reducción de hasta un 20% de emisiones de gases de efecto invernadero y energía eléctrica en 2020. Como parte del ecosistema urbano, la gestión del ciclo del agua no sólo debe garantizar el suministro de agua potable y el tratamiento de agua residual sino que debe hacerlo de manera sostenible, limitando su impacto ambiental y los costes asociados. Las actividades del ciclo urbano el agua incluyen la captación del agua, su potabilización, su transporte y distribución hasta el consumidor, la red de alcantarillado y el tratamiento del agua residual y su retorno al medio. Estas actividades son esenciales en cualquier sistema urbano para garantizar el suministro de agua potable y asegurar la calidad del agua para su retorno al medio. Por lo tanto, la gestión del agua en las ciudades debe responder a legislaciones cada vez más estrictas sobre la calidad del agua, como la Directiva sobre Sustancias Prioritarias (Directiva 2008/105/EC) en relación al abastecimiento de agua potable, o la directiva de tratamiento de aguas residuales (Directiva 91/271/EEC), ambas incluidas en la Directiva Marco de Agua (Directiva 2000/60/EC). As a response to the challenge, the AQUAENVEC project proposed to integrate environmental and economic assessment into a comprehensive study of the eco-efficiency of the urban water cycle. This knowledge can help managers and policy-makers when deciding on water issues, for example, whether it is worth or not to improve water quality standards at the expense of more cost, energy and chemicals consumption. Como respuesta a este reto, el proyecto AQUAENVEC proponía integrar el análisis de impacto ambiental y económico en el estudio de la eco-eficiencia del ciclo urbano del agua. Este conocimiento puede ayudar a planificadores y gestores en la toma de decisiones en el sector del agua, por ejemplo, al decidir sobre si reducir los límites de ciertos parámetros de calidad de agua comprendiendo el impacto indirecto asociado a mayores costes económicos y mayor consumo de energía y químicos en el tratamiento. 06 07 02 THE AQUAENVEC PROJECT EL PROYECTO AQUAENVEC Eco-efficiency assessment was carried out integrating environmental and economic indicators. Environmental impact indicators were quantified through LCA while the system value was studied through LCC, quantifying both the construction and operation and maintenance costs. El estudio de eco-eficiencia se realizó integrando indicadores ambientales y económicos. Los indicadores de impacto ambiental se cuantificaron a través del ACV mientras que el valor del sistema se estudió a través del LCC, cuantificando los costes tanto de la construcción como de la operación y mantenimiento. OBJECTIVES Provide decision-making tools to optimise eco-efficiency, through environmental and economic analysis thus ensuring a sustainable management of urban water cycle. OBJETIVOS Proporcionar una herramienta de ayuda a la decisión para optimizar la eco-eficiencia, mediante el análisis ambiental y económico, asegurando una gestión sostenible del ciclo urbano del agua. SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES OBJETIVOS ESPECÍFICOS Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) and impact reduction potential of urban water cycle. Análisis de Ciclo de Vida (ACV) y potencial de reducción de impacto del ciclo urbano del agua. Life Cycle Costing (LCC) and evaluation of cost savings in the urban water cycle. Análisis de los Costes de Ciclo de Vida (LCC) e identificación de potenciales ahorros en el ciclo urbano del agua. Environmental, economic and eco-efficiency indicators to support decision making and promote sustainable use of natural resources and reuse of end products. Indicadores ambientales, económicos y de ecoeficiencia que ayuden a la toma de decisiones y promuevan el uso sostenible de recursos y la reutilización de productos finales. User-friendly tool development to support policy-makers and public and private water managers. Herramienta de evaluación de la eco-eficiencia para gestores públicos y privados del ciclo urbano del agua. Global Warming Potential / Potencial de calentamiento global (kg CO2 eq.) Ciclo de vida METHODOLOGIES Based on the concept of creating more value with less impact, the ISO 14045:2012 on eco-efficiency assessment links the environmental impact with the value of a given system. In the Aquaenvec project, a Life Cycle thinking approach was followed to quantify both environmental impacts and costs of urban water cycle activities. METODOLOGÍAS Eutrophication Potential Ozone Layer Depletion / Potencial de eutrofi- Potential / Potencial zación (kg PO43- eq.) de agotamiento de la capa de ozono (kg CFC-11 eq.) Construction costs / Costes de construcción (€) Operation and maintenance costs / Costes de operación y mantenimiento (€) Besides the application of the eco-efficiency methodology to the main case studies, other methodologies were applied to hundreds of facilities in order to better understand the relationship between environmental or technical issues and economic indicators. For example, Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) was applied to a set of wastewater treatment plants in order to know if a water treatment facility is operating efficiently both from the environmental and economic perspective. DEA is a linear programming methodology to measure the efficiency of multiple decision-making units (i.e. WWTPs) when the productive process shows a structure that is composed of multiple inputs transformed in outputs. Además de la aplicación de la metodología de eco-eficiencia a los principales casos de estudio, se aplicaron otras metodologías a cientos de instalaciones para entender mejor las relaciones entre aspectos ambientales o técnicos y económicos. Por ejemplo, el Análisis Envolvente de Datos (DEA) se aplicó a un conjunto de estaciones depuradoras para saber si las instalaciones operan de manera eficiente, tanto desde la perspectiva ambiental como la económica. DEA es una metodología de programación lineal para medir la eficiencia de múltiples unidades de decisión (por ejemplo, EDARs), cuando el proceso productivo se compone de múltiples inputs que se transforman en outputs. The factors determining the operation and maintenance cost of urban water activities were identified and quantified through the econometric and statistical study of costs from more than 100 water facilities. Therefore, a set of cost functions were obtained in order to estimate with 5 or 6 parameters the cost of operation and maintenance of a water network or treatment plant. Los factores determinantes del coste de la operación y mantenimiento de las actividades del ciclo urbano del agua se identificaron y cuantificaron a través de estudios econométricos y estadísticos de los costes de más de 100 instalaciones de agua. Entonces se pudieron obtener un conjunto de funciones de coste para estimar, a partir de 5 o 6 parámetros, el coste de la operación y mantenimiento de una planta de tratamiento. Basada en el concepto de crear más valor con menor impacto ambiental, la norma ISO 14045:2012 sobre análisis de eco-eficiencia relaciona el impacto ambiental con el valor del sistema estudiado. En el proyecto Aquaenvec, se ha aplicado el concepto de Ciclo de Vida para cuantificar los impactos ambientales y los costes de las actividades del ciclo urbano del agua. Cumulative Energy Demand / Demanda acumulada de energía (MJ eq.) Operational data Datos operacionales Economic data Datos económicos Drinking water treatment plants / Estaciones potabilizadoras 221 17 Supply networks / Redes de abastecimiento 690 20 Sewer networks / Redes de saneamiento 400 28 Wastewater treatment plants / Depuradoras 474 41 > Number of water facilities included in a database for DEA and econometric methodologies application. > Número de instalaciones incluidas en la base de datos para aplicar el DEA y las metodologías econométricas. 08 09 CASE STUDIES: BETANZOS AND CALAFELL CASOS DE ESTUDIO: BETANZOS Y CALAFELL DESCRIPTION 03 DESCRIPCIÓN Con el objetivo de mejorar la eco-eficiencia del ciclo urbano del agua, se realizaron análisis ambientales y económicos en dos ciudades de tamaño pequeño-mediano. Las ciudades seleccionadas fueron Betanzos y Calafell, ubicadas respectivamente en la región Atlántica y Mediterránea que, por lo tanto, presentan diferente clima, calidad de agua y patrón de consumo de agua. la población puede incrementar hasta 5 veces la de invierno debido al turismo. Tiene clima Mediterráneo con una pluviometría media de 575 mm/año y agricultura de regadío. Calafell es una ciudad costera de 24.984 habitantes (1.194 habitantes/km2) con una fuerte estacionalidad, en verano Betanzos está entre dos ríos y tiene 13.537 habitantes con poca variación estacional. Tiene un clima oceánico con pocos periodos secos y una pluviometría media de 1.021 mm/año. En el municipio existen zonas rurales, siendo la densidad de población de 555,81 habitantes/km2 y la agricultura de secano. BETANZOS (GALICIA) CALAFELL (CATALONIA) In order to work towards better eco-efficiency in the urban water cycle, an environmental and economic assessment was performed on two small-medium cities. Betanzos and Calafell cities in the Atlantic and Mediterranean regions respectively, present different climate, water quality and water use patterns. Calafell is a coastal city of 24,984 inhabitants (1,194 inhabitants/ km2) with a strong seasonality, during summer population can increase 5 fold because of tourism. It has Mediterranean climate with an average rainfall of 575 mm/year, and mostly irrigated agriculture. Betanzos is surrounded by rivers and has 13,537 inhabitants with almost no seasonal variation of population. It has oceanic climate, few dry periods and an average rainfall of 1021 mm/year. Rural areas exist, the population density is 555.81 inhabitants/ km2 and it has mostly rain-fed agriculture. Supplied water per citizen [m /inhabitant·year] 3 Betanzos Calafell 110 145 0.07 4 - 109 120 221 77 174 85 134 25,000 7,000 Agua potable suministrada por ciudadano [m /habitante·año] 3 Water production at treatment plant [m3/s] Agua producida en la ETAP [m /s] 3 BETANZOS Length of the transport network [km] Longitud de la red de transporte [km] Length of the distribution network [km] Longitud de la red de distribución [km] Length of the sewer network [km] Longitud del alcantarillado [km] CALAFELL Collected water per citizen [m3/inhabitant·year] Agua residual recogida por ciudadano [m /habitante·año] 3 WWTP Equivalent population Habitantes equivalentes de la EDAR 10 11 DATA COLLECTION RECOGIDA DE DATOS RESULTS RESULTADOS Data collection for these two case studies aimed at compiling as much data as possible at a process-unit level over the urban water cycle activities for the LCA and the LCC. El inventario en los dos casos de estudio, tuvo como objetivo recoger datos muy detallados a nivel de unidades de proceso del ciclo urbano del agua tanto para el ACV como para el LCC. The study comprised construction and operation and maintenance phases of water facilities. The inventory took one and a half years and it was carried out with the collaboration of Betanzos and Calafell city councils as well as the entities that manage their water activities: Viaqua, Sorea and Consorci Aïgues Tarragona. The main data collected was related to flows and costs of: El estudio consideró tanto las fases de Construcción como de Operación y mantenimiento. Durante un año y medio, se trabajó en la recogida de datos con el Concello de Betanzos y el Ayuntamiento de Calafell, así como las entidades que gestionan parte del ciclo urbano en estas dos ciudades: Viaqua, SOREA y el Consorci d’Aigües de Tarragona. Los principales datos recogidos hacen referencia a los flujos y/o costes asociados a: A panel of environmental, economic and eco-efficiency indicators for the urban water cycle were obtained as a result of the LCA and LCC application to both case studies. Each urban water cycle stage was studied separately in terms of environmental impacts and then the environmental indicators were integrated to LCC results for the eco-efficiency analysis. Como resultado de la aplicación del ACV y el LCC en los ciclos urbanos del agua de ambos casos de estudio, se obtuvo un panel de indicadores ambientales, económicos y de eco-eficiencia. Se estudiaron los impactos ambientales de cada etapa del ciclo urbano del agua por separado y después se integraron los indicadores ambientales con los económicos para el análisis de la eco-eficiencia. Calafell and Betanzos’ global environmental and economic indicators: Indicadores ambientales y económicos globales de Calafell y Betanzos: CONSTRUCTION: OPERATION AND ENERGY / ENERGÍA MAINTENANCE: CHEMICALS AND MATERIALS / ELECTROMECHANICAL OPERACIÓN Y PRODUCTOS QUÍMICOS Y MATERIALES EQUIPMENT / EQUIPOS MANTENIMIENTO: WATER / AGUA INFRASTRUCTURE / CONSTRUCCIÓN: INFRAESTRUCTURA ELECTROMECÁNICOS WASTE AND SLUDGE / RESIDUOS Y FANGOS PERSONNEL / PERSONAL REPLACEMENTS / REPOSICIONES Two monitoring campaigns were performed in both case studies during one week each, on July 2013 and January/ February 2014 respectively. It was measured the real emission of methane and nitrous oxide, both greenhouse gases (GHG), at some sewer network points as well as along all the unit-processes of the WWTPs. Also PPCPs were measured at WWTP inlet and outlet waters and sludge. Se realizaron en las dos ciudades dos campañas experimentales, de dos semanas de duración cada una, en Julio 2013 y Enero/Febrero 2014. Se midieron metano y óxido nitroso, ambos gases de efecto invernadero (GEI) en diferentes puntos de la red de alcantarillado y en todas las unidades de proceso de ambas depuradoras, así como la concentración de productos de higiene personal y farmacéuticos (PPCPs) en la depuradora. Global Warming Potential Eutrophication Potential Ozone Layer Depletion Potential Cumulative Annual life Energy Demand cycle costs [tons CO2 eq./year] [tons PO43- eq/year] [g CFC-11 eq/year] [TJ/year] [€/year] Calafell 3,970 100.8 339.2 66.0 8,719,207 € Betanzos 1,820 34.0 91.3 30.5 2,772,185 € Includes construction, operation and maintenance. / Incluye construcción, operación y mantenimiento. Calafell’s urban water cycle presents higher global environmental impacts and costs than Betanzos. These differences are mainly due to its higher population, especially during summer season. El ciclo urbano del agua de Calafell presenta mayores impactos globales y costes asociados. Estas diferencias se deben principalmente a que su tamaño es mayor que el de Betanzos, especialmente en el periodo estival. Nevertheless, a separate analysis of each environmental indicator helped arising some interesting conclusions regarding urban water stages. As an example, related to carbon footprint (Ton CO2/year), sanitation activities have higher emissions than water treatment and supply. Sin embargo, analizando cada indicador ambiental por separado se pueden concluir aspectos interesantes respecto a las diferentes etapas del ciclo urbano del agua. Por ejemplo, con respecto a la huella de carbono (Tn CO2/año), el saneamiento presenta mayores emisiones que el abastecimiento de agua potable. BETANZOS AND CALAFELL CARBON FOOTPRINT AND TOTAL LIFE CYCLE COSTS HUELLA DE CARBONO Y COSTES DEL CICLO URBANO DEL AGUA DE CALAFELL Y BETANZOS Wastewater treatment Betanzos 725 tons CO2 eq./year 0.57 million €/year Calafell 1923 tons CO2 eq./year 1.22 million €/year Drinking water treatment Betanzos 716 tons CO2 eq./year 0.46 million €/year Calafell 481 tons CO2 eq./year 1.27 million €/year Sewer network Betanzos 242 tons CO2 eq./year 1.11 million €/year Calafell 1238 tons CO2 eq./year 3.42 million €/year Supply network Betanzos 137 tons CO2 eq./year 0.63 million €/year Calafell 328 tons CO2 eq./year 2.81 million €/year 12 13 When taking into account environmental issues in decision-making it is relevant to look at other environmental impact indicators besides carbon footprint. Drinking water treatment presents higher contribution to Ozone Layer Depletion due to chlorinated compounds used in disinfection while WWTP has higher impacts on eutrophication due to the nutrients discharge within the effluent. Al incluir aspectos ambientales en la toma de decisiones es importante considerar otros impactos ambientales además de la huella de carbono. La potabilización presenta una mayor contribución en el agotamiento de la capa de ozono por el uso de productos clorados en la desinfección mientras que la depuración tiene mayor contribución sobre los impactos de eutrofización debido a la concentración de nutrientes en el efluente. La perspectiva de ciclo de vida es necesaria para mejorar los impactos y costes de las actividades del ciclo urbano del agua. En este sentido, los impactos ambientales y económicos de la fase de construcción de las plantas (ETAP y EDAR) son ínfimos comparados con los de la operación y mantenimiento. Sin embargo, en el caso de las redes, la fase de construcción es relevante tanto en su impacto ambiental como económico. Además, los materiales y la solución constructiva usada en las redes, determina posteriormente el impacto ambiental y económico asociada al mantenimiento. Life cycle costs of Calafell / Costes del ciclo de vida en Calafell Drinking water treatment Supply network 15% Urban water cycle stages contribution in Betanzos results / Contribución de las etapas del ciclo del agua en resultados de Betanzos 33% 85% 100 % Sewer network 80 % 67% Wastewater treatment 11% 20% 60 % ISO 14045:2012 certification of eco-efficiency results of Betanzos and Calafell urban water cycles, being the first national reference by AENOR Certificación ISO 14045:2012 de los resultados de eco-eficiencia de los ciclos urbanos de Betanzos y Calafell, siendo la primera referencia de certificación nacional por AENOR Water treatment for Calafell supply shows up twice the cost than Betanzos drinking water treatment while the impact is much higher. At DWTP Ampolla lots of chlorinated chemicals are used for disinfection and this high up the ozone depletion layer impact but the cost does not show the same trend. 80% 4 89% 20 % 120 Ozone Layer Depletion Potential Cumulative Energy Demand Life Cycle Costs A life cycle approach is necessary to improve environmental and economic performance of water activities. In this regard, environmental and economic impacts linked to plants construction (DWTP and WWTP) are negligible compared to their operation and maintenance. However, in the case of networks, construction phase does matter both for environmental and economic indicators. Actually the materials and constructive solutions adopted in networks determine afterwards the environmental and economic performance of their maintenance. Drinking water treatment Supply network Sewer network Wastewater treatment In the integration environmental and economic results according to the eco-efficiency ISO 14045:2012, several indicators and graphic representations arose. While rates such as kg CO2/€ are difficult to interpret when comparing different systems, eco-efficiency graphic representations proved to be more inspiring. En la integración de resultados ambientales y económicos según la ISO 14045:2012 de eco-eficiencia, surgieron muchos indicadores y representaciones gráficas posibles. Mientras ratios como los kg CO2/€ son difíciles de interpretar, especialmente cuando se comparan sistemas muy diferentes, las representaciones gráficas de la eco-eficiencia fueron mucho más inspiradoras. 100 100 80 2 60 40 1 20 0 Calafell Betanzos Drinking water treatment Construction / Construcción Operation and maintenance / Operación y mantenimiento Calafell Betanzos Calafell Supply network Betanzos Calafell Betanzos Sewer network Annual life cycle costs Calafell Betanzos Wasterwater system Global Warming Potential [kg CO2 eq./inhabitant·year] Eutrophication Potential Annual Life Cycle Cost [million €/year] Global Warming Potential Urban water cycle eco-efficiency portfolio / Mapa de eco-eficiencia del ciclo urbano del agua 3 Ozone Layer Depletion Potential [g CFC-11 eq./year] 0% Sin embargo, los indicadores por habitante permiten comparar mejor municipios diferentes y son más fáciles de comunicar. Como ejemplo, aunque las dos ciudades presentan ratios de km/habitante similares, la red de alcantarillado de Calafell requiere más energía de bombeo y por lo tanto, tiene mayor coste y huella de carbono por habitante que Betanzos. Ozone layer depletion potential vs. Annual life cycle costs / Potencial agotamiento capa ozono vs. costes anuales de ciclo de vida 140 El mapa de eco-eficiencia permite relacionar los indicadores ambientales y económicos a través de un gráfico x-y. Aunque los resultados de eco-eficiencia de los dos casos de estudio no se pueden comparar debido a sus diferencias, esta representación gráfica es útil para mostrar tendencias y fijar unos puntos de referencia a partir de los cuales poder comparar sistemas similares. Nevertheless, indicators per inhabitant prove to be more comparable between different cities and friendlier in order to disseminate results. As an example, although both cities present similar rates of km/inhabitant, Calafell’s sewer network requires more pumping and therefore has higher costs and carbon footprint per inhabitant than Betanzos. La potabilización en Calafell muestra un coste anual casi dos veces mayor que en Betanzos si bien el impacto ambiental es notablemente muy superior. En este caso, la potabilizadora de Calafell utiliza gran cantidad de compuestos clorados que aumentan notablemente el impacto en este indicador, si bien el coste no se ve incrementado en la misma medida. 40 % Eco-efficiency portfolio allows linking environmental and economic indicators, through an x-y graphic. Even eco-efficiency results from the case studies couldn’t be compared because of their differences; graphic representation is useful in order to show trends and to set reference points of environmental and economic performances in order to compare them within similar systems. 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 20€ 40€ 60€ 80€ 100€ 120€ 140€ 160€ Cost [€/inhabitant·year] Drinking water treatment Sewer network Calafell Supply network Wastewater treatment Betanzos 14 15 04 AQUAENVEC TOOL HERRAMIENTA AQUAENVEC WHAT IS THE AQUAENVEC TOOL FOR? ¿PARA QUÉ SIRVE LA HERRAMIENTA AQUAENVEC? A SET OF ECO-EFFICIENCY INDICATORS / PANEL DE INDICADORES DE ECO-EFICIENCIA Resources Recursos One of the main results of the project is the AQUAENVEC tool: a user-friendly web tool developed to support decision-makers to assess and improve the eco-efficiency of water activities in the urban context. The tool is devoted to policy makers and public and private water managers to provide them a set of environmental, economic and eco-efficiency indicators in a very comprehensive way for a more sustainable decision-making. Uno de los principales resultados del proyecto es la herramienta Aquaenvec: una herramienta web desarrollada para ayudar en la toma de decisiones analizando la eco-eficiencia de las actividades del ciclo urbano del agua. La herramienta está destinada a planificadores y gestores públicos y privados del sector del agua, proporcionándoles indicadores ambientales, económicos y de eco-eficiencia de una forma sencilla, para una toma de decisiones más sostenible. WHAT IS THE AQUAENVEC TOOL ABOUT? ¿QUÉ ES LA HERRAMIENTA AQUAENVEC? URBAN WATER CYCLE / CICLO URBANO DEL AGUA Decision-making Toma de decisiones Energy Energía OPEX FACILITY INSTALACIÓN URBAN URBANO CORPORATE COMPAÑÍA CITIZEN HABITANTE CAPEX Eutrophication Eutrofización FACILITY / INSTALACIÓN Choose to study the urban water cycle or to analyse the performance of single water facilities. / Permite estudiar el ciclo del agua a nivel municipal o centrarse en una instalación en concreto. SUPPORT DECISION-MAKING / AYUDA A LA TOMA DE DECISIONES Climate change Cambio climático Ozone depletion Agotamiento de la capa de ozono SCENARIO ANALYSIS / ANÁLISIS DE ESCENARIOS CITY / CIUDAD GET YOUR REPORT / OBTENCIÓN DE INFORMES Excel VS. PDF Compare projects results for alternative scenarios or timeline analysis. / Compara diferentes proyectos para analizar escenarios alternativos o la evolución temporal. Word Identify the best practices to improve water facilities management and planning. / Identifica las mejores prácticas para mejorar la gestión y planificación de las instalaciones. ECO-EFFICIENCY TOOL / HERRAMIENTA DE ECO-EFICIENCIA HOW TO GET STARTED? ¿CÓMO SE EMPIEZA? LCA ACV LCC ACC ECO-EFFICIENCY ECO-EFICIENCIA OPERATIONAL DATA AND COSTS / DATOS DE OPERACIÓN Y COSTES Type and number of appurtenances of a network./ Tipo y cantidad de accesorios de la red. Innovative eco-efficiency approach, integrating economic and environmental assessment. / Un innovador enfoque de eco-eficiencia, relacionando el impacto ambiental y económico. LIFE CYCLE PERSPECTIVE / PERSPECTIVA DE CICLO DE VIDA FACILITY CHARACTERISTICS / CARACTERÍSTICAS DE LA INSTALACIÓN CHEMICALS CONSUMPTION WATER FLOWS (INPUT-OUTPUT) CHEMICALS CONSUMPTION FLUJOS DE AGUA (ENTRADA-SALIDA) Access to the online tool and watch the video presentation here: Accede a la herramienta online y visualiza el video de presentación aquí: Length, materials and pipe sizes of a network. / Longitud, materiales y diámetros de las tuberías de red. Unit processes and dimensions of a plant. / Unidades de proceso y dimensiones de la planta. http://www.life-aquaenvec.eu/the-aquaenvec-tool/ CONSTRUCTION CONSTRUCCIÓN OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE OPERACIÓN Y MANTENIMIENTO Improve the existing facilities management or design new ones. / Analiza la gestión de las instalaciones existentes o el diseño de nuevas infraestructuras. SLUDGE AND WASTE PRODUCTION PRODUCCIÓN DE FANGOS Y RESIDUOS ENERGY CONSUMPTION AND PRODUCTION CONSUMO Y GENERACIÓN DE ENERGÍA 16 17 05 COMMUNICATION ACTIVITIES ACTIVIDADES DE COMUNICACIÓN Numerous communication and networking activities were carried out during the entire project, aiming to disseminate the project’s results and enhance the transferability of the knowledge to final end-users and stakeholders. 18 Oral presentations at conferences Ponencias en congresos NETWORKING AND STAKEHOLDERS GRUPOS DE INTERÉS Y CONTACTOS 7 Notice Boards located at case studies Carteles explicativos en los casos de estudio Numerosas actividades de comunicación y networking han sido llevadas a cabo a lo largo del proyecto, con el objetivo de difundir los resultados y realizar la transferencia del conocimiento adquirido a los usuarios finales y grupos de interés. DISSEMINATION AND PUBLICATIONS DIFUSIÓN Y PUBLICACIONES 50 8 Attended events Eventos asistidos Aquaenvec tool presentation Presentación herramienta Aquaenvec Organised events Eventos organizados 22 Aquaenvec final event 44 participants Evento final Aquaenvec 44 asistentes 10 Aquaenvec final event 110 participants Evento final Aquaenvec 110 asistentes Torre Agbar, Barcelona 21.05.2015 XXXIII Jornadas AEAS, Burgos, Spain April 2015 Poster presentations at conferences Posters presentados en conferencias 4 notice boards installed 4 carteles explicativos colocados Betanzos, Galicia Spain 3 notice boards installed 3 carteles explicativos colocados Calafell, Tarragona Spain CEA, Santiago de Compostela 28.05.2015 Published scientific papers Artículos científicos publicados Water research Science of the Total Environment Journal of Cleaner Production Water Resources Management Environmental Impact Assessment Review Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering Poster presentation Presentación poster IWA World Water Congress, Lisbon September 2015 18 2 19 Brochures (presentation and results) Folletos (presentación y resultados) 4 +70 Press Releases Notas de prensa Articles in General and Local Media Artículos en medios generalistas y locales Brochure with Aquaenvec’s project results Folleto con los principales resultados del proyecto Aquaenvec 11 2 06 OUTCOMES BENEFICIOS NEWS & PRESS NOTICIAS Y MEDIOS Networking events Eventos de networking The AQUAENVEC project provided valuable knowledge on how to integrate environmental and economic indicators to perform an Eco-efficiency Assessment according to ISO14045:2012. El proyecto Aquaenvec ha generado valioso conocimiento sobre cómo integrar indicadores ambientales y económicos para realizar análisis de eco-eficiencia de acuerdo con la ISO 14045:2012. The eco-efficiency assessment provides information to both private and public urban water managers in order to support decision-making processes when building and operating water facilities. Having different environmental indicators together with economic indicators in an easy and understandable way promotes a more sustainable water management. El análisis de eco-eficiencia aporta información a gestores del ciclo urbano del agua públicos y privados para la ayuda a la toma de decisiones cuando se construyen y se operan instalaciones del ciclo. Disponer de diferentes indicadores ambientales junto con indicadores económicos de una manera fácil y entendible, fomenta una gestión más sostenible del ciclo del agua. Aquaenvec project participants Colaboradores del proyecto Aquaenvec Project meeting Reunión de proyecto Newsletters Boletines RECOGNITION RECONOCIMIENTO Best on-going European project 2013 European Projects Association (EPA) · Diploma guardonats 2013 Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya · Best of the best life texts LIFE 20th anniversary contest · Finalists for Premis Ciències Ambientals Activitat de recerca. Article in general media Artículo en medios generalistas 2 2 TV report Reportaje en TV Radio interview Entrevista en la radio SOCIAL NETWORKING REDES SOCIALES 40 +100 Receiving the EPA’s award for the Best European on-going Project 2013 in Brussels, June 2013 Entrega del premio al mejor proyecto europeo en curso por la EPA, en Bruselas, Junio de 2013 Data updated at June 2015. / Datos actualizados a Junio 2015. ABC Galicia June 2015 Tweets Mentions Menciones Find more information at Para más información visita www.life-aquaenvec.eu Santiago de Compostela 2013 ISO 14045:2012 certification of eco-efficiency results of Betanzos and Calafell urban water cycles and of the developed methodology. Development of a user-friendly web tool that easily assesses eco-efficiency of urban water activities. Communication and stakeholders implication: water utilities, administration and academia collaboration. IWA World Water Congress, Lisbon 2015 Certificación según la ISO 14045:2012 de los resultados de eco-eficiencia de los ciclos urbanos de Betanzos y Calafell, así como la metodología desarrollada. Desarrollo de una herramienta web que analiza fácilmente la eco-eficiencia de las actividades del ciclo urbano del agua. Comunicación e implicación de los grupos de interés: colaboración de empresas de agua, administración y académicos.