How to Stop the Bleeding
Anuncio

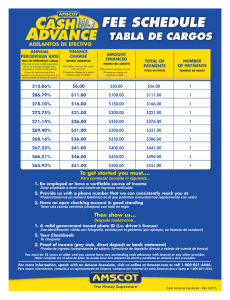
© 2016 Safety Meeting Outlines, Inc. How to Stop the Bleeding There are a lot of opportunities to get cut on a construction site; sharp objects and rough edges are all around. Misusing or mishandling sharp tools can also lead to cuts and puncture wounds. Occasionally, even when we are careful, cuts, lacerations, and puncture wounds still occur and they all bleed. Do you know what to do to control mild or severe bleeding? Before you start first aid, always call 911, or have someone else call for you. Here are several techniques that you can use to stop or at least slow down the bleeding until professional help arrives. Direct Pressure: Most external bleeding can be controlled by direct pressure over the wound. Place a sterile gauze dressing directly over the wound and press against it. If a sterile gauze dressing is not available, use a handkerchief, towel, or any clean cloth that is available. If the bleeding soaks through the gauze or bandage, add another one on top of it. Don’t remove the gauze. Keep pressing firmly on the area. Elevation: If bleeding persists, continue applying direct pressure and elevate the extremity above the level of the heart. When you do this, gravity helps reduce blood pressure and slows bleeding to allow clotting. Be aware that elevation alone will not stop bleeding. And remember that you should not move a broken extremity. Pressure Points: If bleeding still continues, press down at a pressure point while still applying direct pressure to the NOTES: wound. A pressure point exists where an artery is near the skin’s surface, and where it passes close to a bone against which it can be compressed. Tourniquet: Use a tourniquet as a last resort to save a life, only when all other methods have failed. Tourniquets are rarely, if ever, necessary. A tourniquet can damage nerves and blood vessels and may cause the loss of an arm or leg. If you have been trained to apply a tourniquet, do so very carefully and never use rope or wire. No matter what kind of wound you’re dealing with, don’t remove any large or deeply embedded objects. Don’t examine the wound with your hands or any object. If possible, wear latex gloves or vinyl gloves, or use other methods to protect yourself from contact with the victim’s blood. Afterwards, wash your hands with soap and water. It is better to avoid getting injured than to have to control the bleeding. Prevent injuries by following safe work practices and wearing the necessary personal protective equipment. Keep in mind that while wearing the right cutresistant gloves can help you avoid cuts, it’s also really important to actually pay attention to what you’re doing and to watch where you’re putting your hands. SAFETY REMINDER On the jobsite: Do you know where the nearest first-aid kit is located? At home: Is your first-aid kit stocked? MEETING DOCUMENTATION: SPECIAL TOPICS /EMPLOYEE SAFETY RECOMMENDATIONS/NOTES: JOB NAME: MEETING DATE: SUPERVISOR: ATTENDEES: S.A.F.E. CARDS® PLANNED FOR THIS WEEK: REVIEWED MSDS # SUBJECT: These instructions do not supersede local, state, or federal regulations. PO Box 700 Frankfort, IL 60423 815-464-0200 www.safetymeetingoutlines.com Weekly Safety Meetings © 2016 Safety Meeting Outlines, Inc. Quiz Questions How to Stop the Bleeding 1. A tourniquet: a. is usually necessary when someone is bleeding. b. can damage nerves and blood vessels. c. should be made with a rope or a wire. d. should be used in combination with direct pressure. MY ANSWER: __________ CORRECTED ANSWER: __________ 2. When applying direct pressure, if the bleeding soaks through the gauze or bandage, you should: a. stop applying pressure. b. remove the soaked gauze or bandage. c. examine the wound with your hands or with a nearby object. d. add another gauze or bandage on top of it. MY ANSWER: CORRECTED ANSWER: __________ MY ANSWER: 3. True or False? Always start first aid before you call 911. __________ __________ CORRECTED ANSWER: __________ 4. The elevation technique used to stop bleeding: a. involves elevating the extremity above the level of the heart. b. can be used alone to stop bleeding. c. should be used even on broken extremities. d. increases blood pressure to allow clotting. MY ANSWER: CORRECTED ANSWER: __________ 5. True or False? No matter what kind of wound you’re dealing with, you should not remove any large or deeply embedded objects. TRAINER/SUPERVISOR: __________ MY ANSWER: __________ CORRECTED ANSWER: __________ I conducted the safety meeting and administered this quiz. I explained the correct answers and answered or noted every attendees’ question. Signature ____________________________ EMPLOYEE: I understand the material covered in this week’s safety meeting and this quiz. I‘ve written in the correct answers for any questions I initially missed and understand why they are correct. Signature ____________________________ NAME: ID#: TRAINER: SUPERVISOR: PO Box 700 Frankfort, IL 60423 DATE: 815-464-0200 www.safetymeetingoutlines.com Weekly Safety Meetings © 2016 Safety Meeting Outlines, Inc. Answer Key How to Stop the Bleeding 1. A tourniquet: a. is usually necessary when someone is bleeding. b. can damage nerves and blood vessels. c. should be made with a rope or a wire. d. should be used in combination with direct pressure. A tourniquet can damage nerves and blood vessels and may cause the loss of an arm or leg. 2. When applying direct pressure, if the bleeding soaks through the gauze or bandage, you should: a. stop applying pressure. b. remove the soaked gauze or bandage. c. examine the wound with your hands or with a nearby object. d. add another gauze or bandage on top of it. If the bleeding soaks through the gauze or bandage, add another one on top of it. 3. True or False? Always start first aid before you call 911. Before you start first aid, always call 911, or have someone else call for you. 4. The elevation technique used to stop bleeding: a. involves elevating the extremity above the level of the heart. b. can be used alone to stop bleeding. c. should be used even on broken extremities. d. increases blood pressure to allow clotting. If bleeding persists, continue applying direct pressure and elevate the extremity above the level of the heart. 5. True or False? No matter what kind of wound you’re dealing with, you should not remove any large or deeply embedded objects. No matter what kind of wound you’re dealing with, don’t remove any large or deeply embedded objects. FURTHER DISCUSSION: SUPERVISOR/TRAINER NOTES: PO Box 700 Frankfort, IL 60423 815-464-0200 www.safetymeetingoutlines.com © 2016 Safety Meeting Outlines, Inc. Cómo detener una hemorragia (How to Stop the Bleeding) Hay muchas posibilidades de cortarse en una obra de construcción; hay objetos punzocortantes y bordes en mal estado en todas partes. El uso indebido o el mal manejo de herramientas punzocortantes también puede resultar en cortaduras y heridas por perforación. De vez en cuando, incluso cuando tengamos cuidado, las cortaduras, laceraciones, y heridas por perforación pueden suceder y todas comienzan a sangrar. ¿Sabe qué hacer para controlar una hemorragia leve o severa? Antes de iniciar los primeros auxilios, siempre llame al 911, o pídale a alguien más que haga la llamada. Aquí les damos varias técnicas que pueden usar para detener o por lo menos reducir el sangrado hasta que llegue la ayuda profesional. Presión directa: La mayoría de las hemorragias externas pueden controlarse poniendo presión directa sobre la herida. Coloque una venda con gasa estéril directamente encima de la herida y oprima sobre ella. Si no hay una venda de gasa estéril disponible, use un pañuelo, toalla, o cualquier pedazo de tela limpia disponible. Si la sangre empapa y pasa por la gasa o vendaje, añada otra capa encima. No quite la gasa. Mantenga presión firmemente sobre el área. Elevación: Si persiste el sangrado, continúe aplicando presión directa y eleve la extremidad por arriba del nivel del corazón. Al hacer esto, la fuerza de gravedad ayuda a reducir la presión sanguínea y reduce la hemorragia permitiendo la coagulación. Pero tenga en cuenta que la elevación por sí sola no detendrá una hemorragia. Y recuerde que no debe mover una extremidad fracturada. Puntos de presión: Si la hemorragia continúa, oprima en un punto de presión mientras sigue poniendo presión directa en NOTES: la herida. Existe un punto de presión en donde una arteria se encuentra cerca de la superficie de la piel y en donde pasa cerca de un hueso contra el cual se puede hacer presión. Torniquete: Use un torniquete como último recurso para salvar una vida, únicamente cuando los otros métodos no han resultado exitosos. Los torniquetes ocasionalmente, si es que nunca, son necesarios. Un torniquete puede dañar los nervios y vasos sanguíneos y puede causar la pérdida de un brazo o pierna. Si lo han entrenado para usar un torniquete, hágalo con mucho cuidado y nunca use una cuerda o cable. No importa el tipo de herida que tiene que atender, no saque ningún objeto grande o profundamente enterrado. No examine la herida con las manos o con algún objeto. Si es posible, use guantes de látex o guantes de vinilo, o use otros métodos para protegerse de hacer contacto con la sangre de la víctima. Después, lávese las manos con agua y jabón. Es mejor evitar lastimarse que tener que controlar una hemorragia. Prevenga las lesiones siguiendo prácticas de seguridad en el trabajo y usando el equipo de protección personal necesario. Tome en cuenta que al usar el tipo correcto de guantes resistentes a cortaduras puede ayudarlo a evitar una cortadura, también es muy importante realmente poner atención a lo que está haciendo y tener cuidado donde coloca sus manos. SAFETY REMINDER En la obra: ¿Conoce la ubicación del botiquín de primeros auxilios más cercano? En casa: ¿Está debidamente surtido su botiquín de primeros auxilios? MEETING DOCUMENTATION SPECIAL TOPICS /EMPLOYEE SAFETY RECOMMENDATIONS/NOTES: JOB NAME: MEETING DATE: SUPERVISOR: ATTENDEES: S.A.F.E. CARDS® PLANNED FOR THIS WEEK: REVIEWED MSDS # SUBJECT: These instructions do not supersede local, state, or federal regulations. PO Box 700 Frankfort, IL 60423 815-464-0200 www.safetymeetingoutlines.com Weekly Safety Meetings © 2016 Safety Meeting Outlines, Inc. Quiz Questions Cómo detener una hemorragia 1. Un torniquete: a. generalmente es necesario cuando alguien está sangrando. b. puede dañar nervios y vasos sanguíneos. c. se debería hacer con una cuerda o un cable. d. se debería usar en combinación con presión directa. MI RESPUESTA: __________ RESPUESTA CORRECTA: __________ 2. Al aplicar presión directa, si la sangre empapa la gasa o vendaje, usted debe: a. dejar de aplicar presión. b. quitar la gasa o venda empapada. c. examinar la herida con sus manos o con algún objeto cercano. d. añadir otra capa de gasa o vendaje encima de la otra. MI RESPUESTA: __________ RESPUESTA CORRECTA: __________ 3. ¿Verdadero o Falso? Siempre empiece a proporcionar primeros auxilios antes de que usted llame al 911. MI RESPUESTA: __________ RESPUESTA CORRECTA: __________ 4. La técnica de elevación utilizada para detener la hemorragia: a. involucra elevar la extremidad por arriba del nivel del corazón. b. puede ser usada únicamente para detener la hemorragia. c. debería ser utilizada aun cuando haya extremidades fracturadas. d. aumenta la presión sanguínea para permitir la coagulación. MI RESPUESTA: __________ RESPUESTA CORRECTA: __________ 5. ¿Verdadero o Falso? No importa el tipo de herida que tiene que atender, usted no debe sacar ningún objeto grande o profundamente enterrado. MI RESPUESTA: __________ RESPUESTA CORRECTA: __________ ENTRENADOR/SUPERVISOR: Yo llevé a cabo la junta de seguridad y repartí este examen. Expliqué la respuesta correcta y contesté o anoté cada pregunta de los asistentes presentes. Firma _____________________________________________ EMPLEADO: Entiendo el material cubierto en la junta de seguridad de esta semana y en este examen. He llenado las respuestas correctas de toda pregunta que inicialmente tuve mal y entiendo la razón de la respuesta correcta. Firma _____________________________________________ NAME: ID#: TRAINER: SUPERVISOR: PO Box 700 Frankfort, IL 60423 DATE: 815-464-0200 www.safetymeetingoutlines.com Weekly Safety Meetings © 2016 Safety Meeting Outlines, Inc. Answer Key Cómo detener una hemorragia 1. Un torniquete: a. generalmente es necesario cuando alguien está sangrando. b. puede dañar nervios y vasos sanguíneos. c. se debería hacer con una cuerda o un cable. d. se debería usar en combinación con presión directa. Un torniquete puede dañar los nervios y vasos sanguíneos y puede causar la pérdida de un brazo o pierna. 2. Al aplicar presión directa, si la sangre empapa la gasa o vendaje, usted debe: a. dejar de aplicar presión. b. quitar la gasa o venda empapada. c. examinar la herida con sus manos o con algún objeto cercano. d. añadir otra capa de gasa o vendaje encima de la otra. Si la sangre empapa y pasa por la gasa o vendaje, añada otra capa encima. 3. ¿Verdadero o Falso? Siempre empiece a proporcionar primeros auxilios antes de que usted llame al 911. Antes de iniciar los primeros auxilios, siempre llame al 911, o pídale a alguien más que haga la llamada. 4. La técnica de elevación utilizada para detener la hemorragia: a. involucra elevar la extremidad por arriba del nivel del corazón. b. puede ser usada únicamente para detener la hemorragia. c. debería ser utilizada aun cuando haya extremidades fracturadas. d. aumenta la presión sanguínea para permitir la coagulación. Si persiste el sangrado, continúe aplicando presión directa y eleve la extremidad por arriba del nivel del corazón. No importa el tipo de herida que tiene que 5. ¿Verdadero o Falso? No importa el tipo de herida que tiene que atender, usted no debe sacar ningún objeto grande o profundamente atender, no saque ningún objeto grande o profundamente enterrado. enterrado. FURTHER DISCUSSION: SUPERVISOR/TRAINER NOTES: PO Box 700 Frankfort, IL 60423 815-464-0200 www.safetymeetingoutlines.com