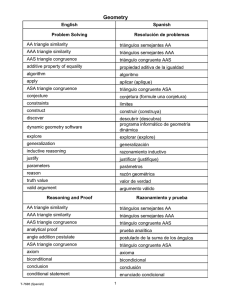
triangle
Anuncio
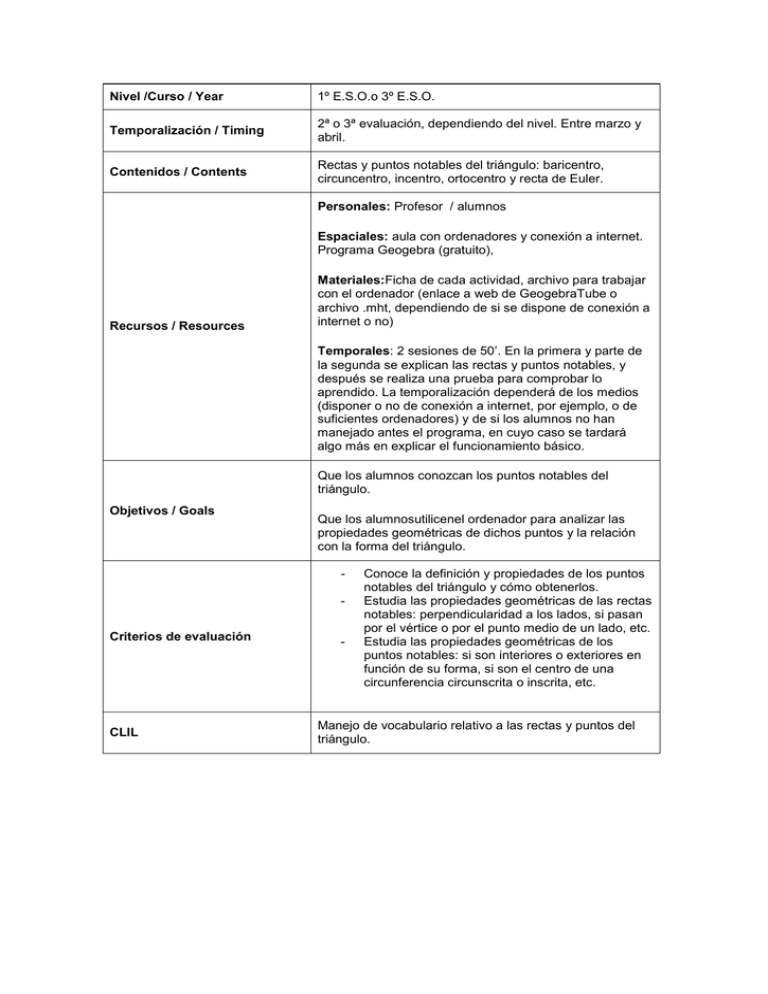
Nivel /Curso / Year 1º E.S.O.o 3º E.S.O. Temporalización / Timing 2ª o 3ª evaluación, dependiendo del nivel. Entre marzo y abril. Contenidos / Contents Rectas y puntos notables del triángulo: baricentro, circuncentro, incentro, ortocentro y recta de Euler. Personales: Profesor / alumnos Espaciales: aula con ordenadores y conexión a internet. Programa Geogebra (gratuito), Recursos / Resources Materiales:Ficha de cada actividad, archivo para trabajar con el ordenador (enlace a web de GeogebraTube o archivo .mht, dependiendo de si se dispone de conexión a internet o no) Temporales: 2 sesiones de 50’. En la primera y parte de la segunda se explican las rectas y puntos notables, y después se realiza una prueba para comprobar lo aprendido. La temporalización dependerá de los medios (disponer o no de conexión a internet, por ejemplo, o de suficientes ordenadores) y de si los alumnos no han manejado antes el programa, en cuyo caso se tardará algo más en explicar el funcionamiento básico. Que los alumnos conozcan los puntos notables del triángulo. Objetivos / Goals Que los alumnosutilicenel ordenador para analizar las propiedades geométricas de dichos puntos y la relación con la forma del triángulo. - Criterios de evaluación CLIL - Conoce la definición y propiedades de los puntos notables del triángulo y cómo obtenerlos. Estudia las propiedades geométricas de las rectas notables: perpendicularidad a los lados, si pasan por el vértice o por el punto medio de un lado, etc. Estudia las propiedades geométricas de los puntos notables: si son interiores o exteriores en función de su forma, si son el centro de una circunferencia circunscrita o inscrita, etc. Manejo de vocabulario relativo a las rectas y puntos del triángulo. FIRSTPART ACTIVITIES 1 2 3 4 5 Centroid - GeoGebraTube.mht Circumcenter - GeoGebraTube.mht Incenter - GeoGebraTube.mht Orthocenter - GeoGebraTube.mht Euler line - GeoGebraTube.mht SECONDPART 1. Translate SPANISH ENGLISH Circuncentro Triángulo rectángulo Centroid Vertex Bisectriz Midpoint Perpendicular bisector 2.- Fill in the gaps. The ______________________ is the center of the circle which passes through the three vertex of the triangle ( ______________ ). __________________ is the point where the three angle bisectors of a triangle meet. __________________ is the center of gravity of the triangle or ______________ . The orthocenter of an obtuse triangle is ___________ the triangle. In any triangle, the ______________ , _____________ and _______________ always lie on a straight line, called the _______ ________ . 3. True or false? The incenter is always inside the triangle. T F The incenter can’t lie on the Euler line. T F The centroid is the epicenter of a triangle. T F A median of a triangle is a line segment joining a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. T F Every triangle has one altitude. T F The circumcenter of a right triangle lies exactly at the midpoint of the hypotenuse. T F 4. Draw Construct the circumcircle of a triangle with compass and ruler: - Draw a triangle. - Draw the perpendicular bisector of the sides of your triangle. - Use the compass to draw the circumcircle.