conditionals
Anuncio

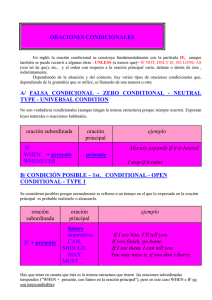
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Las Oraciones Condicionales FIRST CONDITIONAL (TYPE 1) CONDITINAL CLAUSE RESULT CLAUSE Future (will) If + Present Simple Examples If I don´t travel this summer, I´ll regret it. Modal If you take a strager´s bag, it might be dangerous. Present I f you want to buy a ticket, it costs $100. Imperative Study hard if you want to succesd. EL PRIMER CONDICIONAL Su estructura es If + presente + futuro y se usa para indicar que algo se cumplirá con seguridad si la condición también se cumple. If I miss the bus, I will take a taxi. No importa el orden en que se coloque el resultado y la condición, pero si esta aparece primero, es necesario poner siempre una coma entre ambas partes. Cuando la condición se expresa en forma negativa se puede utilizar unless (si no, a menos que, a no ser que) en lugar de if. Unless the weather is good, we won´t play tennis. Variaciones del Primer Condicional. Son posibles algunas variaciones de la estructura básica del primer condicional (ver tabla más arriba) a) If + presente + modal b) If + presente + presente c) If + presente + imperativo 1 ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO SECOND CONDITIONAL (TYPE 2) CONDITINAL CLAUSE If + Past Simple RESULT Examples CLAUSE Conditional (would) If you travelled, you would meet people. EL SEGUNDO CONDICIONAL Su estructura es If + pasado + condicional y se usa para indicar condiciones hipotéticas referidas al presente, es decir que podrían tener lugar pero es poco probable que lleguen a término. If I had more time, I would study German. En español se usa el pretérito imperfecto de subjuntivo en lugar del pasado. Si el verbo de la oración subordinada es to be se puede utilizar were con todas las personas. If she were older, she would get the job. Siempre se usa were con el pronombre I cuando damos un consejo. If I were you, I would talk to him about this problem. Variaciones del Segundo Condicional. Las variaciones más frecuentes de la estructura básica del segundo condicional son los verbos modales could y might, pero estos denotan que la probabilidad de que la hipótesis se cumpla es todavía menor que si se usa would. Es español equivalen a las expresiones “tal vez” , “quizás”. If you studied, you could/might get good results. 2 ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO THIRD CONDITIONAL (TYPE 3) CONDITINAL CLAUSE If + Past Perfect RESULT CLAUSE Conditional Perfect (would have + pp) Examples If I had been more careful, I would have refused to take the bag.. EL TERCER CONDICIONAL Su estructura es If + past perfect + conditional perfect. En este caso la hipótesis es imposible, dado que se refiere al pasado y, por lo tanto, ya no puede realizarse. If he had explained it to us, it wouldn´t have been so complicated. Variaciones del Tercer Condicional. Las variaciones posibles de la estructura básica del tercer condicional son could y might + have + past participle en la oración subordinada. He could have borrowed my car if he had asked. 3 ENGLISH DEPARTMENT / IES FRANCISCO DE QUEVEDO TIME CLAUSES Las Oraciones Temporales TIME CLAUSES TIME CLAUSE When Before Present After + Until Pr. Perfect As soon as By the time MAIN CLAUSE Future (will) Examples As soon as I have finished my homework, I´ll call you. Modal You should take an umbrella before you leave. Present After you´ve passed the exam, you reveive a diploma. Imperative Check to see that you have got your tickets before you leave. LAS ORACIONES TEMPORALES Estas oraciones subordinadas que van introducidas por las conjunciones y expresiones temporales when, as soon as, before, after, until, etc. Llevan el verbo en present simple o present perfect, mientras que la oración principal suele ir en futuro. We will check the exercise when everybody finishes. Variaciones. Las variaciones posibles de esta estructura afectan al verbo principal,que puede ser: a) un modal b) un verbo en presente c) un imperativo (Ver tabla de más arriba para ejemplos). 4