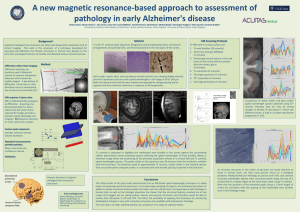
NERVOUS SYSTEM KNOW YOURSELF NERVOUS TISSUE • Nervous System is made of nervous tissue. • And nervous tissue is made up of: 1. NEURONS: the cells that are able to transmit the nervous impulse (electricity). 2. GLIAL CELLS: cells of different kinds with specific functions. 3. EXTRACELLULAR MEDIUM: mixture of substances that contain nutrients and waste products and surround the cells. NEURONS • The main parts are: 1. Dendrites: numerous and small prolongations that have the function of receiving stimuli. 2. Soma: the central part of the neuron that processes the information. 3. Axon: usually 1 single prolongation that transmits the nervous impulse to the next neuron. 4. Axon Terminals: ends of the axon to communicate with other neurons. SYNAPSES • Is the way neurons communicate by 2 ways: electricity and chemical substances (neurotransmitters). • Is formed by: 1. The end of the first neuron (presynaptic terminal). 2. A gap between neurons (synaptic cleft). 3. The beginning of the second neuron (postsynaptic terminal). • To jump the synaptic cleft, neurotransmitters are needed, that are going to join to specific receptors in the next neuron. SYNAPSES GLIAL CELLS • There are 4 kinds: 1. Astrocytes--> essential cells for the nervous tissue because they perform several functions: a. Support for the tissue b. Provide glucose to the neurons c. Eliminate neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft 2. Microglia--> small cells that kill pathogens, so they defend the tissue. 3. Oligodendrocytes--> cells that surround axons in the central nervous system. 4. Schwann cells--> cells that surround axons in the peripheral nervous system. PARTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CENTRAL (CNS) PERIPHERAL (PNS) • Brain • Nerves • Spinal Cord • Ganglions BRAIN • Is the most complex organ of the body and sends orders to other elements. • Is surrounded by a fluid with nutrients called cerebrospinal fluid, produced in the cerebral ventricles. • Is protected by 3 membranous layers called meninges and by the skull, because is very valuable. PARTS OF THE BRAIN 1. CEREBRAL CORTEX: • Is the biggest and most evolved part of the brain. It has many foldings, that can host millions of neurons. • Receives information from many other parts of the brain and sends information to them. When it reaches the cerebral cortex, become conscious. • Perform voluntary movements and sensations become conscious when they reach this part. PARTS OF THE BRAIN 1. CEREBRAL CORTEX: • Is responsible of superior mental abilities: reasoning, association, memory, learning, planification... • There are specialized areas for certain functions, that activate when neccesary. Also, they interchange information with other areas. • Therefore, there are sensitive areas, motor areas, associative areas, reasoning areas, etc. PARTS OF THE BRAIN 1. CEREBRAL CORTEX: PARTS OF THE BRAIN LIMBIC SYSTEM: • Formed by several areas in the brain: amigdala, hippocampus, basal ganglions, etc. 2. • Related to emotions, feelings and linked responses. • Primary emotions and more elaborated ones are developed here. • Connects with the cerebral cortex and other parts of the brain. PARTS OF THE BRAIN 3. CEREBELLUM: • Is a complex structure at the back of the brain that looks like a mini brain. • It has many foldings, similar to the ones of the cerebral cortex. • In charge of complex movements, like driving, riding a bicycle, swimming, playing sports... • Also related to body balance and spacial orientation. PARTS OF THE BRAIN 4. BRAIN STEM • Is the rest of the brain, and is formed by the next parts: I. Thalamus (Tálamo o Diencéfalo) II. Mesencephalus (Mesencéfalo) III. Pons (Puente) IV. Medulla Oblongata (Bulbo Raquídeo) • Thalamus receives information from the 5 senses and transmits a part to the cerebral cortex (is a filter). • The other parts control basic functions as breathing, heart rythm, sleeping... • Cranial nerves start here. SPINAL CORD • Is under the brain stem. • It coordinates movements of different levels of the body. • Also receives sensations. • Sometimes the information passes to the brain, others not (reflexes). • Spinal nerves start here. SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM • Is formed by motor and sensory nerves and ganglions. • Sensory nerves receive information from the receptors of the 5 senses. • Motor nerves transmit orders from the brain to the muscles. • There are also mixed nerves that transmit both sensorial and motor information. AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM • Formed by nerves and ganglions related to the organs of the body. • There are 2 parts: 1. Sympathetic NS it stimulates organs (lungs, heart, digestive system, etc) to work. 2. Parasympathetic NS it inhibits organs (lungs, heart, digestive system, etc) to stop working. RESPONSES • They can be voluntary or involuntary (reflexes). • In voluntary responses cerebral cortex is involved, so the individual realizes about what is happening. • It works like this: Receptors Spinal Cord Brain Muscle/s REFLEXES • They are involuntary. • Spinal Cord is responsible of performing them thanks to sensory neurons, interneurons and motor neurons. • It works like this: Receptors Sensory neuron Interneuron Motor neuron Muscle/s