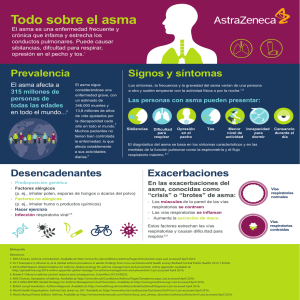
ASMA CASI FATAL Recognition risk for fatal asthma … MR. A. Héctor Ramos Bravo UCI-H.N.E.R.M. ASMA • Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the airways, resulting from the secondary bronchoconstriction 5 - 10% • 2010, approximately 25.7 million Americans were diagnosed with asthma de la población mundial Prevalencia ASTHMA DEATHS IN 2003. 1 Age adjusted to 2000 United States standard population. Njira L Lugogo MD and Neil R MacIntyre MD Life-Threatening Asthma: Pathophysiology and Management FAARC Respir Care2008; 53(6):726 –735. © Asthma Prevalence and Mortality GENERALIDADES SÍNDROME DE ASMA CRÍTICO (CAS), • Status asmático (SA) exacerbación severa asma que no responde fácilmente a terapia intensiva • Asma casi fatal (NFA) ataque al estado asmático que progresa a insuficiencia respiratoria. • Tasa de mortalidad es entre 10% a 25%, principalmente por anoxia y parada cardiopulmonar. • Near-fatal asthma (NFA) and fatal asthma represent the most severe clinical presentations of asthma • Hypercapnia • Acidemia • Altered state of consciousness • Development of cardiorespiratory arrest requiring endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation Nicholas Kenyon Amir A. Zeki Definition of Critical Asthma Syndromes, Clinical Reviews in Allergy & ImmunologyNovember 2013 PRECIPITATING FACTORS FOR SEVERE ASTHMA Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY WILLIAM W. B AND ROBERT A STHMA N Engl J Med, Vol. 344, No. 2001 Asthma Inflammation: Cells and Mediators Peter J. Barnes, MD PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Engrosamiento de membrana basal Hiperplasia de glándula submucosa Descamación del epitelio Hipertrofia del músculo liso Vasodilatación Edema de la mucosa y submucosa, infiltración con eosinófilos, neutrófilos, mastocitos, células mononucleares y células T Tapón de moco Normal CVF FEV1 MARKERS OF SEVERE ASTHMA Anthony D Holley1,2 and Robert J Boots, Review article: Management of acute severe and near-fatal asthma, Emergency Medicine Australasia (2009) 21, CLINICAL FEATURES OF THE TWO KNOWN NEAR-FATAL ASTHMA PHENOTYPES Ruben D. Restrepoa and Jay Peters, Near-fatal asthma: recognition and management Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2008 VENTILATION IN LUNGS WITH AND WITHOUT AIRFLOW OBSTRUCTION Njira L Lugogo MD and Neil R MacIntyre MD Life-Threatening Asthma: Pathophysiology and Management FAARC Respir Care2008; 53(6):726 –735. © 2008 Measurement of intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure Cuando el vaciado pulmonar es lento en relación con el TE disponible resulta entonces, insuficiente para que la PA termine de equilibrarse con la presión atmosférica David R Stather1 and Thomas E Stewart Clinical review: Mechanical ventilation in severe asthma, Critical Care 2005, 9:581-587 (DOI 10.1186/cc3733 REQUIRING HOSPITALIZATION FOR A PATIENT WITH SEVERE ASTHMA Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 MANEJO ASMA CASI FATAL Recognition risk for fatal asthma … MR. A. Héctor Ramos Bravo UCI-H.N.E.R.M. OXIGENO Y B2-AGONISTS R • OXIGENO maintain oxygen saturation above 90%. • Short -acting b2-agonists remains the first line • Continuous nebulization of b2-agonists • MDI with spacer provides equivalent efficacy to nebulized treatments equal to or better than intravenous infusion Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 OXIGENO Y B2-AGONISTS R Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 • SALBUTAMOL genérico SANDOZ) / VENTOLIN Inhalador/ VENTOALDO • Inhalador 100 mcg / inhalación MDI (=suspensión para inhalación envase presurizado) • VENTOLIN Solución Respirador Solución para inhalación por nebulización BROMURO DE IPATROPIO • ampolla contiene 250 microgramos/ml de bromuro de ipratropio, es decir 250 microgramos en 1 ml • 1 ml de solución para nebulizar (= 20 gotas) contiene: Ipratropio Bromuro 0.25 mg. • ATROVENT • Inhalador 20 mcg/inhalación • Bromuro de Ipatropio ANTICHOLINERGIC DRUGS • Anticholinergics and b-agonists produces an improvement in PEFR and FEV1 above that produced by b-agonists alone Rodrigo GJ, Rodrigo C. First line therapy for adult patients with acute asthma receiving a multiple-dose protocol of ipratoprium bromide plus albuterol in the emergency department. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 161:1862– 1868. • B-blockers and monoamine oxidase inhibitors • Onset of action 1 min, peak e 20 min persist 48 h Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 De 40 estudios, 13 seleccionados y ocho de ellos eran de alta calidad. Adición de dosis múltiples de anticolinérgicos a los agonistas beta2 parece seguro, mejora la función pulmonar y evitaría el ingreso hospitalario en 1 de 12 pacientes tratados. 20 ensayos con elegibilidad de la revisión, 2.697 niños. Inhalados anticolinérgicos mas B2 corta experimentan una mayor mejoría de la función pulmonar y menos riesgo de náuseas y temblor. The Cochrane Library 2000, Issue 3 The Cochrane Library 2013, Issue 8 CHANGE FROM BASELINE IN % PREDICTED FEV1, 60 MINUTES AFTER THE LAST OF IB. The Cochrane Library 2013, Issue 8 CORTICOSTEROIDS • Decrease inflammation, increase the number and sensitivity of b-receptors, and inhibit the migration and function of eosinophils • Recommended especially those who do not respond completely tb2-agonist therapy benefits from corticosteroid 6–24 h after administration • May also reduce the number of cases of fatal asthma Inhaled corticosteroid therapy reduces the risk of rehospitalization and all-cause mortality in elderly asthmatics. Eur Respir J 2001 Blais L, Ernst P, Boivin JF, et al. Inhaled corticosteroids and the prevention of readmission to hospital for asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998 INHALED CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY REDUCES THE RISK OF REHOSPITALIZATION AND ALL-CAUSE MORTALITY IN ELDERLY ASTHMATICS Inhaled corticosteroid therapy reduces the risk of rehospitalization and all-cause mortality in elderly asthmatics. Eur Respir J 2001 CORTICOSTEROIDS • ICU setting is the intravenous administration • Methylprednisolone mg c/12 h 80–125mg C/ 6 h 24 h followed 60–80 • Prednisone maintained 1 mg/kg for 7–10 days • Tapering of oral corticosteroids is not necessary in patients who are receiving inhaled corticosteroids and the combined use of the inhaled and oral Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 SYSTEMIC EPINEPHRINE AND TERBUTALINE • Patients unresponsive to continuous nebulized b2-agonists lteration of mental status oran inability to tolerate inhaled therapy • Epinephrine 0.3–0.5 ml (1 : 1000) of epinephrine every 20 min • maximum of three doses. • Terbutaline 0.25–0.5 mg SC pregnant Females • Terbutaline infusion 0.05– 0.10mg/kg/Min • improvement in the clinical the first 24 h, • shorter use of continuous nebulized albuterol, • shorter ICU stay • differences were not statistically significant. Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 METHYLXANTHINES • Theophylline has a very narrow therapeutic to toxic index and significant side effects (vomiting and tachycardia) impending • Respiratory failure who have failed aggressive therapy with inhaled bronchodilators action on the diaphragm and its anti-inflammatory effects • Meta-analyses support no significant additive clinical benefit with the addition of theophylline to a full course of inhaled β-agonists Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 Aminofilina iv no dio lugar a una broncodilatación adicional en los pacientes que experimentan una exacerbación del asma en el ámbito EMERGENCIA Por cada 100 personas tratadas con aminofilina otras 20 personas habían vómitos y 15 personas arritmias o palpitaciones. No se identificaron subgrupos en los que la aminofilina podría ser más eficaz. Nuestra actualización en 2012 es consistente con las conclusiones originales que la relación beneficio-riesgo de aminofilina intravenosa es desfavorable. MAGNESIUM SULFATE • Inhibits calcium channels in smooth muscle and reduces acetylcholine release • 40% of asthmatic patients exhibited magnesium deficiency • Low magnesium erythrocyte concentrations • 2 g of magnesium sulfate is administered over 20 minutes. Repeat doses, if used, require careful monitoring of magnesium level Cochrane meta-analysis • Magnesium sulfate IV improves pulmonary function and decreases hospital admissions in acute severe asthma • Inhaled magnesium sulfate improves pulmonary function during acute exacerbations of asthma, fails outcomes, such as hospital admissions. • Magnesium sulfate can improve pulmonary function modestly and when dosed appropriately has no significant side effect profile Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 16 trials included 896 patients who were randomised. Poca evidencia de que inhaled MgSO4 sustituto de B2 -agonistas Inh. MgSO4 mas B2 -agonistas inhalados (con o sin ipratropio inhalado ), actualmente no existe una clara evidencia general de la función pulmonar mejora o reducido los ingresos hospitalarios. Sin embargo, los resultados de estudios individuales de tres ensayos sugieren una posible mejora de la función pulmonar en aquellos con exacerbaciones graves del asma (FEV1 inferior al 50 % del valor teórico ). El papel más eficaz de MgSO4 nebulizado puede sea en aquellos con características agudas graves y es aquí donde la investigación futura debe centrarse. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012 INTRAVENOUS AND NEBULIZED MAGNESIUM SULFATE FOR TREATING ACUTE ASTHMA IN ADULTS AND CHILDREN: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS. • 25 ensayos (16 por vía intravenosa, 9 nebulizados) la participación de 1.754 paciente • Sulfato de magnesio IV además de β2-agonistas y corticoides sistémicos, en el tratamiento de agudos de asma mejora la función pulmonar y reducir el número de ingresos hospitalarios por los niños, y sólo a mejorar la función pulmonar en adultos • Nebulizacion sulfato de magnesio, seguro, sólo parece producir beneficios para adultos. Shan Z, Rong Intravenous and nebulized magnesium sulfate for treating acute asthma in adults and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis, RESPIRATORI MED. 2013 Mar; 107 (3) :321-30. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed. Epub 2013 03 de enero. HELIOX 8nl R 4 r • Helio y Oxígeno eficaz 70:30 mejora la entrega y disposición de albuterol • He muy baja densidad, que disminuye el flujo turbulento generado por el paso del aire a través de las vías respiratorias constreñidas. disminuir resistencia inspiratorio y espiratorio • asma aguda grave refractaria al tratamiento convencional • aumentar eliminacion de dióxido de carbono barrera endotelial epitelial en comparación con la presencia de una mezcla de oxígeno y nitrógeno como gas portador. • Heliox también se ha demostrado para mejorar la oxigenación, la cual puede permitir que las concentraciones más altas de helio que se entregarán Reuben AD, Harris AR: Heliox for asthma in the emergency department: A review of the literature. Emerg Med J 2004; 21:131135 Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 HELIOX-DRIVEN Β2-AGONISTS NEBULIZATION FOR CHILDREN AND ADULTS WITH ACUTE ASTHMA: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW WITH METAANALYSIS. • Efficacy of heliox versus oxygen in driving β2-agonist nebulization in patients with acute asthma. • 10 studies (697 participants) met the inclusion criteria (7 included adults and 3 included children ) • Peak expiratory flow 95% confidence interval P = .005 • Improvement in PEF compared with those with mild to moderate acute asthma. • Heliox-driven nebulization decreases in the risk of hospitalizations P = .003 and severity of exacerbations P = 0.04 There were no group differences for serious adverse effects. • This review suggests that heliox benefits in airflow limitation and hospital admissions could be considered clinically significant. Data support the use of heliox as a nebulizing β2-agonist driving gas in the routine care of patients with acute asthma. Rodrigo GJ Castro-Rodrigue, Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014 Jan;112(1):29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.anai. Heliox-driven β2-agonists nebulization for children and adults with acute asthma: a systematic review with meta-analysis. . TREATMENT FOR LIFE-THREATENING ASTHMA KETAMINE • Ketamine is an intravenous analgesic agent that has bronchodilator, produce airway relaxation by acting on various receptors and inflammatory cascades, which mediate bronchospasm • May stimulate bronchial secretions and laryngospasm and may cause tachycardia, hypertension, delirium, dissociative state, and lowering of seizure threshold. • It also may be used in life-threatening situations when conventional therapy has failed. Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 • Un único estudio que incluyó a 68 niños no intubados fue elegible para su inclusión en la revisión • no hubo diferencias significativas en la frecuencia respiratoria, saturación de oxígeno, hospital tasa de ingreso y la necesidad de ventilación mecánica entre la ketamina • DOSIS 0,2 mg / kg en bolo intravenoso más de un a dos minutos, seguido de un 0,5 mg / kg por hora de infusión continua durante dos horas • No hubo efectos secundarios significativos de la ketamina en el estudio. existe la necesidad de ensayos aleatorios con suficiente poder estadístico de alta calidad metodológica, con medidas de resultado objetivas de importancia clínica. Los ensayos The Cochrane Library 2012, The Cochrane Library 2012, Ketamina es un potente broncodilatador para ser considerado como una terapia de rescate en el estado asmático refractario. Sin embargo, merece estudios más estudios bien diseñados para determinar su papel en el asma aguda ADJUNCT THERAPIES FOR BRONCHOSPASM Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 NONINVASIVE MECHANICAL VENTILATION • Safe treatment and can reduce the need for intubation in a selected group of patients • Improving alveolar ventilation, decreasing the risk of respiratory muscle fatigue. • Bronchodilation and decreases the airway resistance, reverses atelectasis, and promotes removal of secretions. NPPV • CPAP or PEEP of about 5 cm H2O • Inspiratory pressure 8 cm H2O. If tidal volumes are shallow (<7 mL/kg) • Increased gradually by 2 cm H2O every 15 minutes, • Goal to reduce FR 25 breaths per minute. Peak pressures greater than 15 to 20 cm H2O rarely can be tolerated without mask leaks or discomfort or claustrophobia. Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 • EARLY INITIATION OF NONINVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION, ALONG WITH SHORT ACTING Β-AGONISTS AND SYSTEMIC STEROIDS, CAN BE SAFE, WELL-TOLERATED, AND EFFECTIVE IN THE MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN WITH STATUS ASTHMATICUS Sangita Basnet, MD, FAAP; Gurpreet Mander, Safety, efficacy, and tolerability of early initiation of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation in pediatric patients admitted with status asthmaticus: A pilot study*Pediatr Crit Care Med CONTRAINDICATIONS FOR NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE-PRESSURE VENTILATION Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 MECHANICAL VENTILATION IN ASTHMA PATIENTS MECHANICAL VENTILATION IN ASTHMA PATIENTS MECHANICAL VENTILATION IN ASTHMA PATIENTS • Sedation and analgesia are almost always required in preparation for intubation • Benzodiazepines or propofol and opioids • NMBAs), especially early in their ventilatory course to control respiratory • Concomitant use of corticosteroids and NMBAs typically produces proximal and distal muscle weakness. • intermittent dosing should be used and they should be discontinued as soon as possible • infusions must be stopped every 4 to 6 hours to prevent accumulation • The rationale for neuromuscular blockade is to control the respiratory rate, decrease chest wall stiffness, eliminate muscle loading from patient-ventilator dysynchrony and oxygen consumption, and lower the risk of barotrauma Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 Measurement of intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure Cuando el vaciado pulmonar es lento en relación con el TE disponible resulta entonces, insuficiente para que la PA termine de equilibrarse con la presión atmosférica David R Stather1 and Thomas E Stewart Clinical review: Mechanical ventilation in severe asthma, Critical Care 2005, 9:581-587 (DOI 10.1186/cc3733 David R Stather1 and Thomas E Stewart Clinical review: Mechanical ventilation in severe asthma, Critical Care 2005, 9:581-587 (DOI 10.1186/cc3733 MECHANICAL VENTILATION STRATEGIES Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 COMPLICATIONS OF ACUTE SEVERE ASTHMA Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013 Sujanthy Rajaram Life-Threatening Asthma CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Parrillo and Dellinger Fourth Edition 2013-2014 GRACIAS MR. A. Héctor Ramos Bravo UCI-H.N.E.R.M.