instituto tecnológico superior “david ausubel”
Anuncio

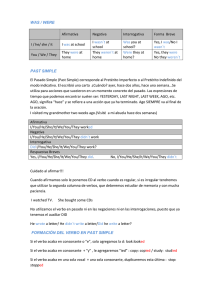
INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO GUIA DE ESTUDIO MODULAR ENGLISH ONE FIRST LEVEL TECNOLOGÍAS EN: ADMINISTRACIÓN DE EMPRESAS MENCIÓN CONTABILIDAD Y AUDITORIA E INFORMÁTICA MENCIÓN ANÁLISIS DE SISTEMAS Desarrollo Guía Modular: Corrección: GRACE AGUIRRE P. Comisión de Redacción Aprobado: Vicerrectorado Académico Edición: Fecha: Instituto Superior Tecnológico “David Ausubel” OCTUBRE 2015 – ABRIL 2016 QUITO - ECUADOR 1 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO PARA USTED APRECIADO ESTUDIANTE NO OLVIDE QUE EL ESFUERZO Y LA PERSEVERANCIA MÁS EL ESTUDIAR Y TRABAJAR ENGRANDECE AL SER HUMANO. Y USTED DEPENDE EL ENGRANDECERSE El Instituto Tecnológico Superior “David Ausubel”, da la bienvenida a este su módulo de Comunicación Oral y Escrita y espera que el desarrollo del mismo aporte para su vida profesional. 2 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO NOTA: EN ESTE TEXTO GUÍA SE ENCUENTRAN DESARROLLADOS LOS TEMAS QUE CORRESPONDEN A ESTE MÓDULO, Y LAS TAREAS QUE USTED DEBE DESARROLLAR; CON LA AYUDA DEL TUTOR USTED LLEGARÁ A DOMINAR EL CONOCIMIENTO. 1. EL ESTUDIANTE TIENE LAS OPORTUNIDADES QUE SEAN NECESARIAS PARA ACLARAR LOS TEMAS QUE NO COMPRENDAN MEDIANTE LA EXPLICACIÓN DEL DOCENTE, YA SEA DE MANERA PRESENCIAL O MEDIANTE EL CORREO ELECTRÓNICO Y LA PLATAFORMA. 2. LAS TAREAS SERÁN ENVIADAS POR EL TUTOR, PREVIA SU EXPLICACIÓN. ES OBLIGACIÓN DEL ESTUDIANTE ASISTIR A CADA UNA DE LAS TUTORIAS PRESENCIALES PROGRAMAS EN EL CALENDARIO DE ACTIVIDADES. 3. TODO TRABAJO DEL ESTUDIANTE SERÁ EVALUADO CUANTITATIVAMENTE. 4. AL FINAL EL DOCENTE EVALUARÁ EL MÓDULO EN SU TOTALIDAD. 5. DE REQUERIR CUALQUIER INFORMACIÓN DIRIGIRSE AL CORREO DEL DOCENTE O DEL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO Y SERÁ ATENDIDO INMEDIATAMENTE EN SU CONSULTA. Docente Grace Aguirre [email protected] [email protected] Gracias por su confianza. 3 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO 1. PERFIL DE CARRERA ADMINISTRACIÓN DE EMPRESAS MENCIÓN CONTABILIDAD Y AUDITORIA. a) OBJETIVO DE FORMACION INTEGRAL DEL PROFESIONAL Formar profesionales con personalidad definida, altos valores éticos, morales, culturales y espíritu emprendedor; preparados científica y tecnológicamente para iniciar y administrar pequeñas y medianas empresas, con aplicación del Mercadeo, Finanzas, Producción y Administración; comprometido con el desarrollo sostenido y sustentable del país. b) PERFIL DEL TECNÓLOGO EN CONTABILIDAD Y AUDITORÍA Es un profesional emprendedor capaz de aplicar sistemas contables y mecanismos de control contable y financiero, sobre bases científico-metodológicas y legales, demostrando espíritu emprendedor y altos valores éticos y morales. c) COMPETENCIAS DEL TECNÓLOGO EN CONTABILIDAD Y AUDITORÍA Demostrar eficiencia en el manejo contable y financiero en el sector empresarial y público Participar en auditorías de la actividad contable y financiera en empresas y organizaciones Adoptar decisiones oportunas en el manejo contable y financiero, en función de la eficiencia y eficacia empresarial Desarrollar los mecanismos de control interno que promuevan la eficiencia, reduzcan los riesgos de pérdida de activos, asegurar la confiabilidad de los estados financieros dentro del marco de cumplimiento de las leyes y regulaciones Administrar su propia microempresa de servicios contables y de auditoría. SISTEMATIZACIÓN DE LAS COMPETENCIAS DEL TECNÓLOGO EN CONTABILIDAD Y AUDITORÍA d) NIVEL COMPETENCIA PRINCIPAL Aplicar correctamente sus conocimientos micro y macro económicos en una planificación estratégica Llevar a cabo proyectos de auditoría en su propia microempresa 4 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO F) ESCENARIOS DE ACTUACION El tecnólogo en Contabilidad y Auditoría podrá desenvolverse en: Empresas del Sector público o privado Empresas nacionales o internacionales Pymes Industrias Bancos Financieras ONGs Centros educativos Su propia microempresa de servicios administrativos Tecnología en Administración de Empresas G) OCUPACIONES PROFESIONALES El tecnólogo en Contabilidad y Auditoría podrá desempeñarse como: Administrador de pequeñas y medianas empresas Director departamental Jefe de oficina Asesor de pequeñas y medianas empresas Funcionario bancario Administrador de su propia microempresa 2. PERFIL DE INFORMÁTICA MENCIÓN ANÁLISIS DE SISTEMAS a) OBJETIVO DE FORMACIÓN INTEGRAL DEL PROFESIONAL Demostrar en el desempeño profesional de la informática un comportamiento ético que se evidencie en el interés por la investigación e innovación tecnológica, con responsabilidad social, espíritu empresarial y compromiso con el desarrollo sostenido y sustentable del país. b) PERFIL DEL TECNÓLOGO EN INFORMÁTICA 5 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO Es un profesional capaz de usar herramientas y técnicas para recolectar datos, analizar, diseñar, desarrollar e implementar nuevos sistemas que permitan automatizar los procedimientos de las empresas con fundamentos científicos, tecnológicos, humanísticos y de gestión, demostrando sólidos valores ético-morales. c) COMPETENCIAS PRINCIPALES POR DESARROLLAR Conducir el ciclo de vida de un sistema de información que permita automatizar el manejo de los datos mediante un sistema de computadora, utilizando para ello las diferentes herramientas informáticas existentes en el medio actual. Fundamentar cambios en la estructura organizacional, procedimientos, políticas y funciones de una entidad que permitan optimizar el flujo de datos e información, aumentando con ello la productividad y competitividad y disminuyendo los costos operativos. Administrar las acciones para realizar un correcto análisis, diseño, desarrollo y documentación de los sistemas informáticos de un centro de cómputo, que cubran las expectativas de la institución y del medio en que se desenvuelve. Evaluar y seleccionar hardware y software, fundamentado en cuadros comparativos técnicos que permitan satisfacer los requerimientos de las empresas y organizaciones en general. Analizar de manera independiente e imparcial las bondades o defectos de un sistema de información, mediante la valoración de todos los procesos que intervienen, tomando en cuenta las necesidades y el presupuesto económico. Apoyar la toma de decisiones de la gerencia utilizando métodos matemáticos, estadísticos, modelos de transporte y de investigación de operaciones. SISTEMATIZACIÓN DE LAS COMPETENCIAS POR NIVELES d) NIVEL COMPETENCIA PRINCIPAL Instalar, operar y administrar programas utilitarios conociendo todos los principios de la informática. Programar en lenguajes de tercera generación aplicando técnicas especializadas y con pleno conocimiento de sistemas matemáticos y contables 6 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO Conocer las acciones requeridas hacia la automatización de las empresas mediante el análisis, diseño, desarrollo, documentación e implementación de los sistemas. Diseñar y administrar Bases de datos, dominando la programación en herramientas de cuarta generación y la programación orientada a objetos. Participar en el diseño de sistemas informáticos interactuando con plataformas de internet y con pleno conocimiento de la administración de las redes y sus sistemas operativos. Administrar las actividades de un departamento de cómputo con la aplicación de herramientas informáticas y gerenciales incluyendo la creación de su propia microempresa. e) ESCENARIOS DE ACTUACIÓN El Tecnólogo en Informática podrá desempeñarse en todo tipo de empresa pública o Privada donde se requiera tratar de una manera especial a los datos y la información que Se generan dentro de la entidad, sea por procesos o por transacciones: ·Instituciones Bancarias Entidades Financieras Empresas Comerciales Empresas del estado Entes de servicio a la comunidad Instituciones de capacitación a nivel profesional, universitario o intermedio Empresas de Asesoría Informática f) OCUPACIONES PROFESIONALES El Tecnólogo en Informática podrá desempeñarse como: Gerente de Sistemas Programador de computadoras Director de grupos de trabajo Administrador de Centros de Cómputo Asistente de gerencia Administrador de Bases de Datos Instructor de personal en el área informática 7 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO Asesor organizacional de las empresas Asesor en el área informática IN FORMATIVES DATES CAREER: BUSINESS ADMINISTRATION ACCOUNTING STATEMENT AND AUDIT AND COMPUTER SYSTEMS ANALYSIS STATEMENT. LEVEL : FIRST LEVEL SPECIALTY : ALL SPECIALTIES ZONE : LANGUAGES SUBJECT : ENGLISH TEACHER : GRACE AGUIRRE P. CREDIT NUMBER : 3 CREDITS 1. FUNDAMENTOS DE LA ASIGNATURA Esta asignatura es fundamental ya que le permitirá al estudiante entender y desarrollar ejercicios con un adecuado uso gramatical, de acuerdo a cada tiempo de la oración (presente y pasado), usando las diferentes aplicaciones del verbo To Be y de la forma Auxiliar: Do, Does y Did, a fin de ejercitar oraciones para posteriores diálogos y conversacionales relacionados con la Especialidad. 2. COMPETENCIAS 2.1. Competencia General.- Establecer bases gramaticales del Idioma Inglés para desarrollar la comunicación oral y escrita en forma correcta. 2.2. Competencias específicas: 2.2.1. UNIT ONE.- SIMPLE PRESENT.- Diferenciar y aplicar los diferentes pronombres personales en oraciones de tiempo presente simple con el verbo To Be: Aplicaciones en preguntas; respuestas afirmativas y negativas cortas y respuestas afirmativas y negativas completas. 2.2.2. UNIT TWO.- SIMPLE PAST.- Diferenciar y aplicar los diferentes pronombres personales en oraciones de tiempo pasado simple con el verbo To Be: Aplicaciones en preguntas; respuestas afirmativas y negativas cortas y respuestas afirmativas y negativas completas. 2.2.3. UNIT THREE.- PRESENT CONTINUOUS.- Diferenciar y aplicar los diferentes pronombres personales, en oraciones de tiempo presente continuo (presente 8 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO progresivo) con el verbo To Be: Aplicaciones en preguntas; respuestas afirmativas y negativas cortas y respuestas afirmativas y negativas completas. 2.2.4. UNIT FOUR.- PAST CONTINUOUS.- Diferenciar y aplicar los diferentes pronombres personales, en oraciones de tiempo pasado continuo (pasado progresivo) con el verbo To Be: Aplicaciones en preguntas; respuestas afirmativas y negativas cortas y respuestas afirmativas y negativas completas. 2.2.5. REGULAR VERBS.- Estudio y análisis de los verbos regulares y su aplicación en los diferentes tiempos de la oración gramatical, con especial énfasis en el uso de terceras personas del singular (He – She – it); excepciones y aplicación. 2.2.6. IRREGULAR VERBS.- Estudio y análisis de los verbos irregulares y su aplicación en los diferentes tiempos de la oración gramatical, con especial énfasis en el uso de los verbos en pasado. 2.2.7. PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE.- Conocimiento y aplicación de cada uno. 2.2.8. PREPOSITIONS OF TIME.- Conocimiento y aplicación de cada uno. 3. CONTENIDOS UNIT ONE.- SIMPLE PRESENT UNIT TWO.- SIMPLE PAST UNIT THREE.- PRESENT CONTINUOUS UNIT FOUR.- PAST CONTINUOUS APPENDIX REGULAR VERBS 9 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO IRREGULAR VERBS PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE PREPOSITIONS OF TIME TIME AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE Present Simple Verb to be I am a student. (Yo) soy un estudiante. You are happy. (Tú) estás feliz. He is in the park. (El) está en el parque. He`s studying now. (El) está estudiando ahora. I’m not a student. You aren’t happy. He isn’t in the park. INTERROGA TIVE Am I a student? Are you happy? Is he in the park? He isn’t studying now. Is he studying now? I was a girl. (Yo) fui una niña. He was sick. (El) estuvo enfermo. They were in Mexico. (Ellos) estuvieron en México. I wasn’t a girl. He wasn’t sick. They weren’t in Mexico. Was I a girl? Was he sick? Were they in Mexico? Present Continuous Past Simple Verb to be 10 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO Past Continuous It was raining. Estaba lloviendo. It wasn’t raining. Was it raining? TO B E UNIT ONE.- SIMPLE PRESENT Note: The verb TO BE has a different form after different subjects. TO BE I AM SIMPLE PRESENT QUESTION SHORT ANSWERS Yes, I am. No, I am not. I`m = I am. I am a student. Am I a student? YOU ARE You are my friend. Are you my friend? Yes, you are. No, you are not. Aren’t = are not. HE He is a new teacher. Is he a new teacher? She is very nice. Is she very nice? It is ok. Is It ok? Yes, He is. No, he isn’t. Yes, She is. No, She isn’t. Yes, it is. No it isn’t. Isn’t = is not. SHE IS IT WE ARE We are the world Are we the world? Yes, we are. No, we aren’t. YOU ARE You are my friends. Are you my friends? Yes, you are. No you aren’t. They are good guys. Are they good guys? THEY ARE EXERCISES: The plane is on time every Mondays. Is it on time every Mondays? Yes, it is. No, it isn’t. Yes, they are. No, they aren’t. Any students are not conscious about their responsibilities. Are they conscious about their responsibilities? Yes, they are. No, they aren’t. 11 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO TIMETABLE: 2 HOURS WRITTEN TESTS: 2 TO BE UNIT TWO.- SIMPLE TO BE I WAS SIMPLE PAST PAST QUESTION I was a student. Was I a student? YOU WERE You were my friend. Were you my friend? HE He was a new teacher. Was he a new teacher? SHE WAS IT She was very nice. Was she very nice? It was ok. Was It ok? SHORT ANSWERS Yes, I was. No, I wasn’t. Wasn’t = was not. Yes, you were. No, you were not. Weren’t = were not. Yes, He was. No, he wasn’t. Yes, She was. No, She wasn’t. Yes, it was. No it wasn’t. Wasn’t = was not. WE WERE We were the world. Were we the world? Yes, we were. No, we weren’t. YOU WERE You were my friends. Were you my friends? Yes, you were. No you weren’t. They were good guys. Were they good guys? Yes, they were. No, they weren’t. THEY WERE EXERCISES: The plane was on time every Mondays. Was it on time every Mondays? Yes, it was. No, it wasn’t. Any students were not conscious about their responsibilities. Were they conscious about their responsibilities? Yes, they were. No, they weren’t. TIMETABLE: 2 HOURS WRITTEN TESTS: 2 12 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO TO B E UNIT THREE.- PRESENT CONTINUOUS Note: The verb TO BE has a different form after different subjects. TO BE SIMPLE PRESENT QUESTION I am studying English. Am I studying English? YOU ARE You are working now. Are you working now? HE He is teaching Math. Is he teaching Math? She is cooking pizza. Is she cooking pizza? It is flying to Manta. Is It flying to Manta? I AM SHE IS IT SHORT ANSWERS Yes, I am. No, I’m not. I`m = I am. Yes, you are. No, you aren’t. Aren’t = are not. Yes, He is. No, he isn’t. Yes, She is. No, She isn’t. Yes, it is. No it isn’t. Isn’t = is not. WE ARE We are buying books. Are we buying books? Yes, we are. No, we aren’t. YOU ARE You are speaking fast. Are you speaking fast? Yes, you are. No, you aren’t. They are listening to music. Are they listening to music? THEY ARE EXERCISES: The plane is arriving on time. Is it arriving on time? Yes, it is. No, it isn’t. TIMETABLE: 2 HOURS Yes, they are. No, they aren’t. The students are playing football. Are they playing football? Yes, they are. No, they aren’t. WRITTEN TESTS: 2 13 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO TO B E UNIT FOUR.- PAST CONTINUOUS Note: The verb TO BE has a different form after different subjects. TO BE I WAS YOU WERE HE SHE WAS IT WE SIMPLE PAST I was studying English. SHORT ANSWERS Yes, I was. Was I studying English? No, I wasn’t. Wasn’t = was not. You were working yesterday. Were you working yesterday? Yes, you were. No, you weren’t. Weren’t = were not. He was teaching Math. Was he teaching Math? She was cooking pizza. Was she cooking pizza? It was flying to Manta. Was It flying to Manta? Yes, He was. No, he wasn’t. Yes, She was. No, She wasn’t. Yes, it was. No it wasn’t. Wasn’t = was not. WERE We were buying books. YOU WERE You were speaking fast. THEY WERE They were listening to music. EXERCISES: The plane was arriving on time. Was it arriving on time? Yes, it was. No, it wasn’t. TIMETABLE: 2 HOURS QUESTION Were we buying books? Yes, we were. No, we weren’t. Were you speaking fast? Were they listening to music? Yes, you were. No, you weren’t. Yes, they were. No, they weren’t. The students were playing football. Were they playing football? Yes, they were. No, they weren’t. WRITTEN TESTS: 2 14 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO REGULAR VERBS IRREGULAR VERBS PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE PREPOSITIONS OF TIME IRREGULAR VERBS INFINITIVE PAST PARTICIPLE MEANING (be) am- is - are Was – were Been Ser, estar arise Arose Arisen Elevarse, surgir, originarse. awake Awoke Awoken Despertar, mover, excitar. beat Beat Beaten Batir,revolver, golpear, vencer. become Became Become Hacerse,tornarse,convertirse en. begin Began Begun Empezar, iniciar. bend Bent Bent Doblar, inclinar, torcer. bite Bit Bitten Morder. blow Blew Blown Soplar break Broke broken Quebrar, partir, romper. 15 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO bring Brought brought Traer, llevar, conducir. build Built built Construir, edificar. burn Burnt burnt Quemar, incendiar. burst Burst burst Romper, reventar. buy Bought bought Comprar catch Caught caught Coger, asir, atrapar. choose Chose chosen Escoger, elegir. come Came come Venir cost Cost cost Costar creep Crept crept Arrastrarse,deslizarse, pegarse. cut Cut cut Cortar, dividir. do Did done Hacer, ejecutar. draw Drew drawn Tirar, arrastrarse, atraer, dibujar. drink Drank drunk Beber drive Drove driven Impulsar, conducir, llevar, inducir. fall Fell fallen Caer, disminuir. feed Fed fed Alimentar, nutrir. feel Felt felt Sentir, percibir, tocar. fight Fought fought Pelear, combatir. find Found found Encontrar, descubrir. fly Flew flown Volar forget Forgot forgotten Olvidar (se) forgive Forgave forgiven Perdonar freeze Froze frozen Congelar get Got got (ten) Lograr, obtener, conseguir. give Gave given Dar, conceder. go Went gone Ir (se), funcionar, resultar. grow Grew grown Crecer, cultivar. have Had had Tener, haber. hear Heard heard Oír, escuchar. hide Hid hid (den) Ocultar, encubrir. hold Held held Sostener,mantener,contener. hurt Hurt hurt Herir, dañar, lastimar. keep Kept kept Mantener,guardar,conservar. know Knew known Conocer, saber. lay Laid laid Poner, colocar. lead Led led Guiar, llevar, conducir. lean Leant leant Inclinar(se), apoyarse. learn Learnt learnt Aprender, saber. leave Left left Partir, irse, abandonar. lend Lent lent Prestar 16 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO let Let let Permitir, conceder. lose lost lost Perder, malgastar. make made made Hacer, confeccionar, producir. mean meant meant Significar,querer decir pretender. meet met met Encontrarse, satisfacer. melt melted molten (old) Derretir(se), fundir(se). mistake mistook mistaken Equivocarse, comprender mal, errar pay paid paid Pagar, recompensar. put put put Poner,colocar, exponer. read read read Leer,descifrar, marcar. rebuild rebuilt rebuilt Reconstruir ride rode ridden Rodar, tener juego, funcionar. ring rang rung Tocar, sonar. rise rose risen Ascender,elevarse,levantarse, surgir. run ran run Correr, funcionar. saw sawed sawn Cortar con sierra, aserrar. say said said Decir, afirmar. see saw seen Ver, observar. sell sold sold Vender send sent sent Enviar set set set Instalar, establecer, colocar, fijar. shake shook shaken Sacudir, lanzar, agitar. shine shone shone Brillar, relumbrar, sobresalir. shoot shot shot Disparar, emitir, lanzar. show showed shown Mostrar, excibir, probar, demostar. sing sang sung Cantar sit sat sat Sentarse, reunirse. sleep slept slept Dormir slide slid slid(den) Resbalar, deslizarse, escabullirse. smell smelt smelt Oler, percibir. speak spoke spoken Hablar, decir. speed sped sped Acelerar, apresurarse. spend spent spent Gastar, consumir, emplear (tiempo). spill spilt spilt Derramar, verter, divulgar. split split split Partir, dividir, separar, reventar. spoil spoilt spoilt Deteriorar, dañar, inutilizar. spread spread spread Extender, esparcir, propagar. stand stood stood Pararse, tolerar, estar (de pié). steal stole stolen Robar, escabullirse. stick stuck stuck Pegar, adherirse, prender, fijar. stink stank stunk Oler mal, apestar. 17 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO strike struck struck Golpear, pegar, estallar. swim swam swum Nadar, flotar. swing swung swung Balancera(se), hacer girar. take took taken Tomar, llevar. teach taught taught Enseñar tear tore torn Romper, despedazar, rasgar. tell told told Decir, contar, narrar. think thought thought Pensar, creer. throw threw thrown Lanzar, tirar, impeler, arrojar. understand understood understood Comprender. undertake undertook undertaken Emprender, comenzar algo. wake woke woke (n) Despertar, excitar. wear Wore worn Gastar(se), consumirse, usar. win Won won Ganar, conquistar. Write wrote written Escribir REGULAR VERBS INFINITIVE PAST / PARTICIPLE MEANING FINAL PRONUNCIATION act Acted Actuar id add Added Sumar, añadir id aid Aided Ayudar id arrest Arrested Arrestar id assist Assisted Ayudar id attend Attended Asistir, ir id address Addressed Dirigirse t advertise Advertised Anunciar t amuse Amused Entretener t approach Approached Acercarse t ask Asked Preguntar, pedir t accompany Accompanied Acompañar d accustom accustomed Acostumbrar d agree agreed Concordar d annoy annoyed Molestar d answer answered Responder d appeal applealed Atraer d appear appeared Aparecer d arrange arranged Arreglar, ordenar d arrive arrived Arribar d board boarded Abordar id balance balanced Equilibrar t 18 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO bark barked Ladrar t bless blessed Bendecir t brush brushed Cepillar t behave behaved Comportarse d believe believed Creer d boil boiled Hervir d breathe breathed Respirar id complete completed Completar id consist consisted Consistir id count counted Contar id close closed Cerrar t cook cooked Cocinar t crash crashed Chocar t cross crosssed cruzar t call called Llamar d care cared Cuidar d carry carried Llevar d change changed Cambiar d check checked Chequear t charge charged cargar, cobrar d clean cleaned Limpiar d climb climbed escalar, subir d comb combed Peinar d cover covered Cubrir d cry cried Llorar d crawl crawled gatear, arrastrarse d dance danced bailar t dress dressed vestir t dropp dropped dejar caer t dial dialed sintonizar, marcar d die died morir d declare declared declarar d delay delayed demorar d deliver delivered entregar d deny denied negar d dine dined cenar d dry dried secar d enclose enclosed incluir, encerrar t enjoy enjoyed disfrutar d engage engaged comprometer d envy envied envidiar d 19 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO express expressed expresar t exclaim exclaimed exclamar d explain explained explicar d fail failed fracasar, fallar d fasten fastended abrochar d file filed archivar d fill filled llenar d fire fired echar del trabajo, disparar d follow followed seguir d frighten frightened espantar d fry fried freir d finish finished terminar t fish fished pescar t fix fixed fixed t guess guessed adivinar t help helped ayudar t hope hoped esperar, desear t happen happened suceder d hurry hurried apurar (se) d imagine imagined imaginar d iron ironed planchar d judge judged juzgar d kiss kissed besar t kill killed matar d laugh laughged reir t leak leaked gotear t like liked gustar t lock locked cerrar con llave t look looked mirar t mark marked marcar, señalar t milk milked ordeñar un animal t miss missed extrañar t manage managed manejar d marry married casar (se) d massage massaged masajear d measure measured medir d move moved mover d observe observed observar d offer offered ofrecer d open opened abrir d order ordered ordenar d 20 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO peform performed ejecutar d phone phoned telefonear d plan planned planear d play played jugar, tocar d pour poured derramar, verter d pray prayed orar d prefer prefered preferir d prepare prepared preparar d pull pulled tirar d park parked estacionar t pass passed pasar t pick picked recoger t please pleased complacer d practise practised practicar t promise promised prometer t pronounce pronounced pronunciar t punish punished castigar t push pushed empujar t repeat repeated repetir id report reported reportar, informar id request requested solicitar, pedir id rest rested descansar id reach reached alcanzar t refuse refused rehusar t raise raised levantar t rain rained llover d realize realized darse cuenta d register registered matricularse, registrar d receive received recibir d Remain remained quedar, sobrar d Remember remembered recordar d Repair pepaired reparar d Require required requerir d Reserve reserved reservar, guardar d Resolve resolved resolver d Return returned retornar, volver d Search searched buscar, registrar t Save saved salvar d serve served servir d sign signed firmar d smile smiled sonreir d 21 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO snow snowed nevar d spill spilled derramar d stay stayed permanecer, quedarse d study studied estudiar d slip slipped resbalar t smoke smoked fumar t stop stopped detener, parar t switch switched conectar, accionar t stretch stretched estirar t talk talked conversar t thank thanked agradecer t touch touched tocar, palpar t tire tired cansar, fatigar d train trained entrenar d travel traveled viajar d trouble troubled molestar d try tried tratar, intantar d turn turned girar, voltear d unpack unpacked desempacar t use used usar t visit visited visitar id wait waited esperar id want wanted querer, requerir id walk walked caminar t wash washed lavar t watch watched observar, mirar t wish wished desear, anhelar t work worked trabajar t warm warmed calentar d warn warned advertir d water watered regar d PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE NOTES on 22 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO in Avobe over under EXERCISES PREPOSITIONS OF PLACE NOTES In front of behind 23 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO beside near next to Between among EXERCISES PREPOSITIONS OF TIME (AT – IN – ON) at for a PRECISE TIME. in for MONTHS, YEARS, CENTURIES and LONG PERIODS. on for DAYS and DATES. at PRECISE TIME in MONTHS, YEARS, CENTURIES on DAYS and DATES 24 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO and LONG PERIODS at 3 o'clock in May on Sunday at 10.30am in summer on Tuesdays at noon in the summer on 6 March at dinnertime in 1990 on 25 Dec. 2010 at bedtime in the 1990s on Christmas Day at sunrise in the next century on Independence Day at sunset in the Ice Age on my birthday at the moment in the past/future on New Year's Eve EXAMPLES I have a meeting at 9am. The shop closes at midnight. Jane went home at lunchtime. In England, it often snows in December. Do you think we will go to Jupiter in the future? There should be a lot of progress in the next century. Do you work on Mondays? Her birthday is on 20 November. Where will you be on New Year's Day? Notice the use of the preposition of time at in the following standard expressions: Expressions Examples at night The stars shine at night. at the weekend I don't usually work at the weekend. at Christmas/Easter I stay with my family at Christmas. at the same time We finished the test at the same time. 25 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO at present He's not home at present. Try later. Notice the use of the prepositions of time in and on in these common expressions: in on in the morning on Tuesday morning in the mornings on Saturday mornings in the afternoon(s) on Sunday afternoons in the evening(s) on Monday evening When we say last, next, every, this we do not also use at, in, on. I went to London last June. (not in last June). He's coming back next Tuesday. (not on next Tuesday). I go home every Easter. (not at every Easter). We'll call you this evening. (not in this evening). 26 INSTITUTO TECNOLÓGICO SUPERIOR “DAVID AUSUBEL” SEMIPRESENCIAL VICERRECTORADO ACADÉMICO New Interchange INTRO A. / Cambridge University Press. New Interchange BOOK 1. / Cambridge University Press. English in Mind 1A / Cambridge University Press. English in Mind 1B / Cambridge University Press. Inglés. Diccionario Ilustrado / Berlitz Publishing. A Communicative Grammar / Interactions one. Focus on Grammar / An Integrated Skills Approach. www.englishclub.com www.lingolex.com 27