NOMBRE DEL TIEMPO TRADUCCIÓN EN USOS MÁS EN INGLÉS
Anuncio
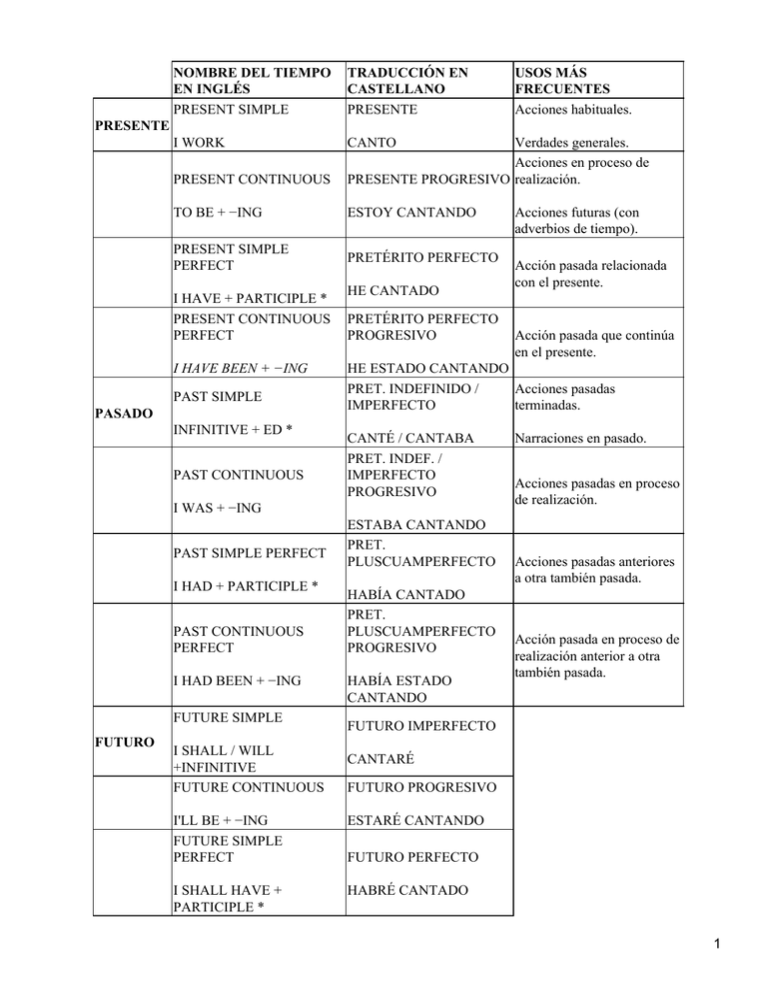
NOMBRE DEL TIEMPO EN INGLÉS PRESENT SIMPLE TRADUCCIÓN EN CASTELLANO PRESENTE I WORK CANTO USOS MÁS FRECUENTES Acciones habituales. PRESENTE PRESENT CONTINUOUS Verdades generales. Acciones en proceso de PRESENTE PROGRESIVO realización. TO BE + −ING ESTOY CANTANDO PRESENT SIMPLE PERFECT PRETÉRITO PERFECTO I HAVE + PARTICIPLE * PRESENT CONTINUOUS PERFECT I HAVE BEEN + −ING PAST SIMPLE PASADO INFINITIVE + ED * PAST CONTINUOUS HE CANTADO PRETÉRITO PERFECTO PROGRESIVO I HAD + PARTICIPLE * PAST CONTINUOUS PERFECT I HAD BEEN + −ING FUTURE SIMPLE FUTURO I SHALL / WILL +INFINITIVE FUTURE CONTINUOUS Acción pasada relacionada con el presente. Acción pasada que continúa en el presente. HE ESTADO CANTANDO Acciones pasadas PRET. INDEFINIDO / terminadas. IMPERFECTO CANTÉ / CANTABA PRET. INDEF. / IMPERFECTO PROGRESIVO I WAS + −ING PAST SIMPLE PERFECT Acciones futuras (con adverbios de tiempo). ESTABA CANTANDO PRET. PLUSCUAMPERFECTO HABÍA CANTADO PRET. PLUSCUAMPERFECTO PROGRESIVO HABÍA ESTADO CANTANDO Narraciones en pasado. Acciones pasadas en proceso de realización. Acciones pasadas anteriores a otra también pasada. Acción pasada en proceso de realización anterior a otra también pasada. FUTURO IMPERFECTO CANTARÉ FUTURO PROGRESIVO I'LL BE + −ING FUTURE SIMPLE PERFECT ESTARÉ CANTANDO I SHALL HAVE + PARTICIPLE * HABRÉ CANTADO FUTURO PERFECTO 1 FUTURE CONTINUOUS PERFECT I SHALL HAVE BEEN + −ING * Es donde van los verbos irregulares. FUTURO PERFECTO PROGRESIVO HABRÉ ESTADO CANTANDO TIEMPOS VERBALES I CORRESPONDENCIA EN INGLÉS En todos los tiempos, donde pone Yo sirve igual para las personas : Tú, Nosotros, Vosotros, Ellos excepto los marcados con los símbolos 1ª, 2ª, 3ª, 4ª o %. En todos los tiempos, donde pone Él sirve igual para las personas : Ella, Ello excepto los marcados con los símbolos 1ª, 2ª, 3ª, 4ª o %. TIEMPO INFINITIVO INFINITIVO PRETÉRITO (perfecto) CASTELLANO Ser/estar AFIRMATIVO INTERROGATIVO NEGATIVO PASIVA Not to be To be Haber/tener To have Trabajar To work Haber sido/estado To have been Haber habido/tenido To have had Haber trabajado To have worked Siendo/estando − ell ser/estar PARTICIPIO PRESENTE Habiendo/teniendo − el Y GERUNDIO tener/estar Trabajando − el trabajar PARTICIPIO PASADO (pasivo) IMPERATIVO Being Having Working Sido/estado Been Habido/tenido Had Trabajado Sé tú Worked Be Sea él − dejadle ser Let him be Not to Ser to be loved have amado Not to work Not have been Not have had To Haber have sido been amado loved Not have worked Not Siendo being amado − el Not Being hecho loved having de ser Not amado working Amado loved Do not be 2 Let not him be Seamos nosotros − dejadnos ser Let us be Sed vosotros Be Sean ellos − dejadlos ser Let them be Ten tú Have Tenga él − dejadle tener Let him have Let not us be Do not be Let not them be Tengamos nosotros − dejadnos Let us have tener Have Tened vosotros Let them have Tengan ellos − dejadlos tener Work Trabaja tú Let him work Trabaje él − dejadle trabajar Let us work Trabajemos nosotros − Work dejadnos trabajar Trabajad vosotros Do not have Let not him have Let not us have Do not have Let them work Let not them have Trabajen ellos − dejadlos trabajar Do not work Let not him work Let not us work Do not work Let not them work REFLEXIVA Yo me lavo Él se lava PRESENTE DE INDICATIVO Yo soy/estoy I wash myself He washes himself I am Am I? I am not Yo I am soy loved 3 Yo he/tengo I have Have I? Yo trabajo I work Do I work? I have amado not I do not work You are not Tú eres/estás Tú has/tienes You have Tú trabajas You work Él es/está He is (pretéritos compuestos del indicativo) Are you? Have you? Do you work? Has he? He has Él trabaja He work Does he work? I was Was I? I had Had I? I worked Worked I? Tú/2ª eras/fuiste/estabas/estuviste You were Yo he sido/estado I have been Yo he habido/tenido I have had Yo he trabajado I have worked Él ha sido/estado He has been Él ha habido/tenido He has had You have not Tú You eres are amado loved You do not work He is not Is he? Él ha/tiene Yo/1ª era/fui/estaba/estuve PRETÉRITO INDEFINIDO (pretérito Yo/% había/hube/tenía/tuve imperfecto i indefinido)* Yo/% trabajaba/trabajé PRETÉRITO PERFECTO You are He has Él He is not es loved amado He does not work I was not I had not Yo/1ª I was era/fui loved amado I did not work Tú/2ªYou You Were you? did not eras/fuiste were loved work amado I have not Have I been? been I Yo he have Have I had? I have sido not had been amado loved Have I worked? I have not worked Has he been? He has Él ha He not sido has Has he had? been amado been 4 Él ha trabajado Yo/% había sido/estado PRETÉRITO Yo/% había habido/tenido PLUSCUAMPERFECTO I had been I had had Had I been? Had I had? Yo/% había trabajado I had worked Had I worked? Yo/3ª seré/estaré I shall be Shall I be? FUTÚRO IMPERFECTO Yo/3ª habré/tendré Yo/3ª trabajaré Él/4ª será/estará Él/4ª habrá/tendrá Él/4ª trabajará Yo/3ª habré sido/estado FUTÚRO PERFECTO He has worked Has he worked? Yo/3ª habré habido/tenido Yo/3ª habré trabajado He has not had loved He has not worked I had not been Yo/% I I had había had not had sido been amado loved I had not worked I shall not be I I shall Yo/3ª shall not seré Shall I have? I shall have be have amado loved I shall worked Shall I work? I shall not worked He will not be Will he be? He will be He He will Él/4ª will Will he have? not He will have be have será/estará loved Will he He will work He will work? not work I shall not have Shall I have been I shall have been? I been I shall Yo/3ª shall habré Shall I have not I shall have had have had? have sido been had amado loved I shall have Shall I have worked worked? I shall not have worked Él/4ª habrá sido/estado 5 Él/4ª habrá habido/tenido Él/4ª habrá trabajado Yo/3ª sería/estaría CONDICIONAL PRESENTE Yo/3ª habría/tendría Yo/3ª trabajaría Él/4ª sería/estaría Él/4ª habría/tendría Él/4ª trabajaría CONDICIONAL PRETÉRITO Yo/3ª habría sido/estado Yo/3ª habría habido/tenido Yo/3ª habría trabajado He will have been Will he have He not been? have been He will have Will he have had been? He not have He will have Will he have had worked worked? He not have worked I should not be Should I be? I should be I Should I should have? I should have not have I should work Should I work? I should not work He would not be Would he be? He He would be would Would he not He would have have? have He would work Would he He work? would not work I should have Should I have I been been? should not I should have Should I have have been had had? I should have worked Él/4ª habrá sido amado He will have been loved I Yo/3ª should sería be amado loved He Él/4ª would sería be amado loved Yo/3ª habría sido amado I should have been loved Should I have I should worked? not have had I should not 6 Él/4ª habría sido/estado Él/4ª habría habido/tenido Él/4ª habría trabajado SUBJUNTIVO PRESENTE SUBJUNTIVO PRETÉRITO PERFECTO He would have Would he been have been? He would have Would he had have had? He would have Would he worked have work? Yo/% sea/estuviera I be Yo/% haya/tenga I have have worked He would not have been He would not have had He Él/4ª would habría have sido been amado loved He would not have worked Yo/% I be sea loved amado I work Yo/% trabaje Yo/% fuera/fuese/estuviera/estuviese Was/were Had Yo/% hubiera/hubiese/tuviera/tuviese Worked Yo/% trabajara/trabajase SUBJUNTIVO PERFECTO SUBJUNTIVO PLUSCUAMPERFECTO Yo/? I were fuera/fuese loved amado Yo/? I have haya been sido loved amado Yo/? I hubiera/hubiese had sido been amado loved * Es donde van los irregulares 1ª Válido para : Yo / Él / Ella / Ello 2ª Válido para : Tú / Nosotros / Vosotros / Ellos 3ª Válido para : Yo / Nosotros 4ª Válido para : Tú / Él / Ella / Ello / Vosotros / Ellos % Válido para : Todas las personas 7 El futuro inglés és perifrástico; se forma con los auxiliares shall (para las primeras personas) y will (para las segundas y terceras personas), seguidos del infinitivo (sin la partícula to) del verbo conjugado. El condicional inglés se forma con los auxiliares should (primeras personas) y would (segundas y terceras personas), más el infinitivo del verbo conjugado. REFLEXIVA (Acción que se realiza uno mismo) (Se hace igual con todos los tiempos) I was myself Yo me lavo You was yourself Tú te lavas He washes himself Él se lava We wash ourselves Nosotros nos lavamos You wash yourselves Vosotros os laváis They wash themselves Ellos se lavan AUXILIARES MODALES O DEFECTIVOS (Sirven para indicar la posibilidad, necesidad, etc., de una acción) (Sólo tienen presente y pretérito indefinido de indicativo) Éstos son: VERBO CASTELLANO PRESENTE CAN puedo MAY MUST OUGHT SHALL WILL puedo (me está permitido) debo (es preciso que) debo (conviene que) debo quiero PRETÉRITO I could I can (puedo) (podía/pude) I might I may (puedo) (podía/pude) NO TIENE I must (debo) PRETÉRITO I ought NO TIENE (debería/debí/debo) PRETÉRITO I shall I should I will I would ESQUEMA GENERAL RESUMIDO INFINITIVO −> ANDAR −> TO +INFINITIVO IMPERATIVO −> ANDES −> QUE +INFINITIVO GERUNDIO −> ANDANDO −> INFINITIVO +ING 8 PASADO −> ANDÉ / ANDABA −> INFINITIVO +ED PARTICIPIO −> ANDADO −> INFINITIVO +ED PERFECT SIMPLE CONTINUOUS SIMPLE CONTINUOUS I am lo que ocurre I have I walk PRESENT acción habitual en este acciones habituales momento concreto I walked PAST FUTURE *infinitivo I will+infi. I was I had I will be I will have (I'll) * Es donde van los irregulares −> Casi no se usan ¿CÓMO SERIA EN CASTELLANO? PERFECT SIMPLE CONTINUOUS SIMPLE CONTINUOUS he PRESENT ando PAST estoy andé / estaba andaba desde antes hasta la actualidad había desde antes hasta antes habré FUTURE andaré estaré desde ahora hasta luego been walking walked *participio pasado walking participio 9 presente estado andando andando andado 10
