el presente perfecto del indicativo
Anuncio

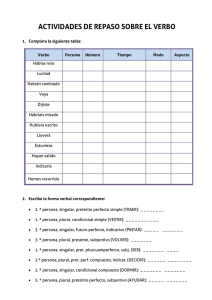
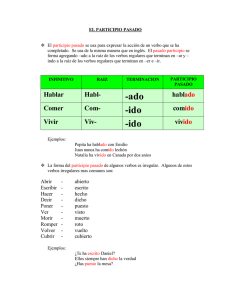
EL PRESENTE PERFECTO DEL INDICATIVO El verbo auxiliar (helping verb) Los verbos regulares forman el presente perfecto al conjugar el verbo auxiliar haber en el presente de indicativo seguido por el participio pasado del verbo. persona pronombre personal haber 1ª singular yo he 2ª singular tú has 3ª singular él, ella, Ud. ha 1ª plural nosotros nosotras hemos 2ª plural vosotros vosotras habéis 3ª plural ellos, ellas, Uds. han PRESENTE PERFECTO = forma de HABER + -ADO/-IDO Modelos de verbos regulares Las formas regulares del presente perfecto del indicativo son: 1ª conjugación singular plural infinitivo: hablar participio: hablado 2ª conjugación infinitivo: beber participio: bebido 3ª conjugación infinitivo: vivir participio: vivido he hablado has hablado ha hablado hemos hablado habéis hablado han hablado singular plural he bebido has bebido ha bebido hemos bebido habéis bebido han bebido singular plural he vivido has vivido ha vivido hemos vivido habéis vivido han vivido Verbos irregulares El uso de un participio pasado irregular es la única irregularidad que ocurre en el presente perfecto. Ejemplos: he abierto has dicho ha hecho hemos puesto habéis roto han visto Los usos del presente perfecto Se usa el presente perfecto para indicar una acción que empezó en el pasado y continúa hasta el presente. Ejemplos: No he visto a Enrique hoy. Todavía no han escrito los ejercicios. Ellos han estado en Madrid tres veces. The present perfect may be used to indicate an action or state as having occurred — and having been completed— prior to the present time. It is used in almost exactly the same way as we use it in English, with TWO EXCEPTIONS: 1. The present perfect is NOT used to indicate an action still in progress. To express an ongoing action which began in the past, the present tense is used: Hace cuatro años que vivo aquí. I have lived (have been living) here for four years. 2. To express the idea “to have just (done something)”, Spanish typically employs the present of acabar de plus the infinitive, for example: Acabo de oír la noticia. I just heard the news [item]. Acabamos de poner el televisor. We have just turned on the TV. Note: acabar literally means to finish or to end.