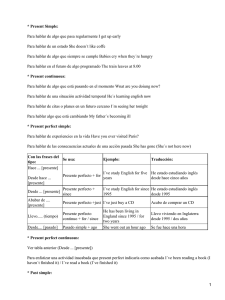
cuadro tenses_ 2º eso - Gobierno de Canarias
Anuncio
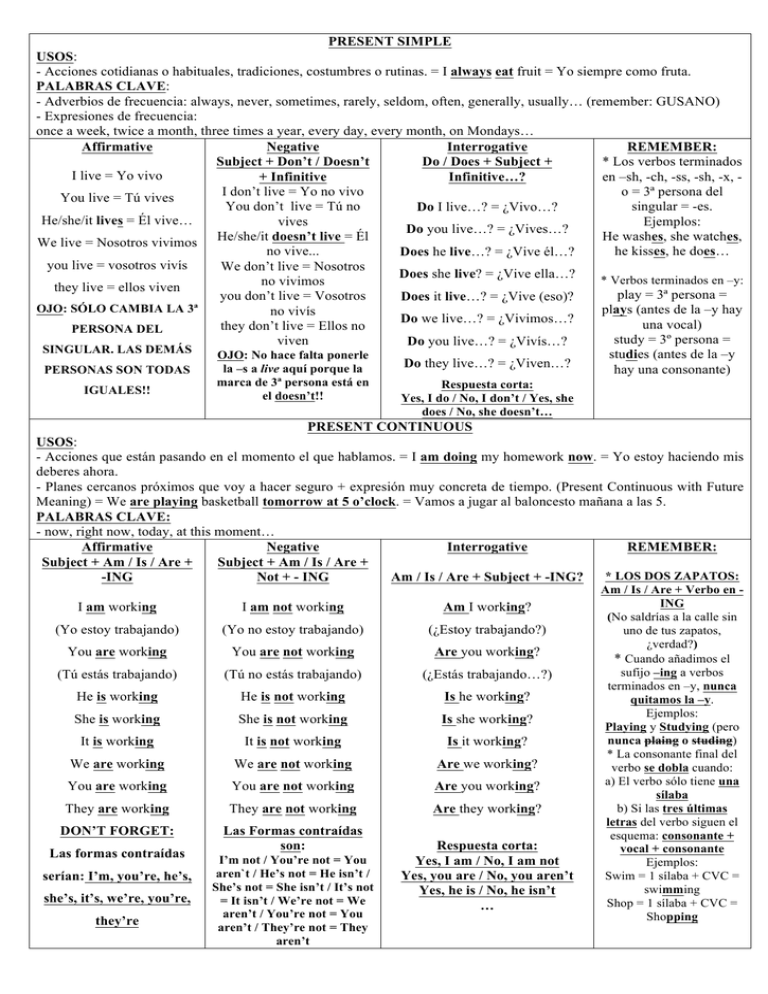
PRESENT SIMPLE USOS: - Acciones cotidianas o habituales, tradiciones, costumbres o rutinas. = I always eat fruit = Yo siempre como fruta. PALABRAS CLAVE: - Adverbios de frecuencia: always, never, sometimes, rarely, seldom, often, generally, usually… (remember: GUSANO) - Expresiones de frecuencia: once a week, twice a month, three times a year, every day, every month, on Mondays… Affirmative Negative Interrogative REMEMBER: Subject + Don’t / Doesn’t Do / Does + Subject + * Los verbos terminados I live = Yo vivo + Infinitive Infinitive…? en –sh, -ch, -ss, -sh, -x, I don’t live = Yo no vivo o = 3ª persona del You live = Tú vives You don’t live = Tú no singular = -es. Do I live…? = ¿Vivo…? He/she/it lives = Él vive… vives Ejemplos: Do you live…? = ¿Vives…? He/she/it doesn’t live = Él He washes, she watches, We live = Nosotros vivimos no vive... he kisses, he does… Does he live…? = ¿Vive él…? you live = vosotros vivís We don’t live = Nosotros Does she live? = ¿Vive ella…? * Verbos terminados en –y: no vivimos they live = ellos viven play = 3ª persona = you don’t live = Vosotros Does it live…? = ¿Vive (eso)? OJO: SÓLO CAMBIA LA 3ª plays (antes de la –y hay no vivís Do we live…? = ¿Vivimos…? una vocal) they don’t live = Ellos no PERSONA DEL study = 3º persona = viven Do you live…? = ¿Vivís…? SINGULAR. LAS DEMÁS studies (antes de la –y OJO: No hace falta ponerle Do they live…? = ¿Viven…? la –s a live aquí porque la hay una consonante) PERSONAS SON TODAS IGUALES!! marca de 3ª persona está en el doesn’t!! Respuesta corta: Yes, I do / No, I don’t / Yes, she does / No, she doesn’t… PRESENT CONTINUOUS USOS: - Acciones que están pasando en el momento el que hablamos. = I am doing my homework now. = Yo estoy haciendo mis deberes ahora. - Planes cercanos próximos que voy a hacer seguro + expresión muy concreta de tiempo. (Present Continuous with Future Meaning) = We are playing basketball tomorrow at 5 o’clock. = Vamos a jugar al baloncesto mañana a las 5. PALABRAS CLAVE: - now, right now, today, at this moment… Affirmative Negative Interrogative REMEMBER: Subject + Am / Is / Are + Subject + Am / Is / Are + * LOS DOS ZAPATOS: -ING Not + - ING Am / Is / Are + Subject + -ING? I am working I am not working Am I working? (Yo estoy trabajando) (Yo no estoy trabajando) (¿Estoy trabajando?) You are working You are not working Are you working? (Tú estás trabajando) (Tú no estás trabajando) (¿Estás trabajando…?) He is working He is not working Is he working? She is working She is not working Is she working? It is working It is not working Is it working? We are working We are not working Are we working? You are working You are not working Are you working? They are working They are not working Are they working? DON’T FORGET: Las Formas contraídas son: Las formas contraídas serían: I’m, you’re, he’s, she’s, it’s, we’re, you’re, they’re I’m not / You’re not = You aren`t / He’s not = He isn’t / She’s not = She isn’t / It’s not = It isn’t / We’re not = We aren’t / You’re not = You aren’t / They’re not = They aren’t Respuesta corta: Yes, I am / No, I am not Yes, you are / No, you aren’t Yes, he is / No, he isn’t … Am / Is / Are + Verbo en ING (No saldrías a la calle sin uno de tus zapatos, ¿verdad?) * Cuando añadimos el sufijo –ing a verbos terminados en –y, nunca quitamos la –y. Ejemplos: Playing y Studying (pero nunca plaing o studing) * La consonante final del verbo se dobla cuando: a) El verbo sólo tiene una sílaba b) Si las tres últimas letras del verbo siguen el esquema: consonante + vocal + consonante Ejemplos: Swim = 1 sílaba + CVC = swimming Shop = 1 sílaba + CVC = Shopping PAST SIMPLE USOS: - Acciones pasadas finalizadas (cerradas): I finished my homework / We went to the cinema yesterday. = Yo terminé mis deberes / Nosotros fuimos al cine ayer. - Acción pasada corta que interrumpió una acción pasada larga. It was raining when we arrived. = Estaba lloviendo cuando llegamos. PALABRAS CLAVE: - yesterday, … ago (two days ago, three years ago), last… (last Monday, last Christmas…), when… Affirmative Negative Interrogative REMEMBER: * Verbos terminados en –y: Subject + Didn’t + Infinitive Did + Subject + Infinitive? play = played (antes de I worked / I drank la –y hay una vocal) I didn’t work / didn’t drink Did I work? / Did I drink? (Yo trabajé / Yo bebí) study = studied (antes de (Yo no trabajé / Yo no bebí) (¿Trabajé…? / ¿Bebí…?) You worked / you drank la –y hay una You didn’t work / didn’t drink Did you work? / Did you drink? (Tú trabajaste / Tú consonante) (Tú no trabajaste / Tú no bebiste) (¿Trabajaste…) / ¿Bebiste…?) bebiste) * Verbos terminados en –e He didn’t work / didn’t drink Did he work? / Did he drink? He worked / He drank sólo añaden una –d. She didn’t work / didn’t drink Did she work? / Did she drink? Ejemplos: She worked / She drank decide = decided; use = It didn’t work / didn’t drink Did it work? / Did it drink? It worked / It drank used; prepare = prepared We didn’t work / didn’t drink Did we work? / Did we drink? We worked / we drank * La consonante final del Did you work? / Did you drink? You worked / you drank You didn’t work / didn’t drink verbo se dobla cuando: They didn’t work / didn’t a) El verbo sólo tiene una Did they work? / Did they drink? They worked / they sílaba drink Respuesta corta: drank OJO: - Todas las personas se conjugan igual. - Para conjugar verbos regulares añadimos –ed o –d al verbo regular. - Para conjugar los verbos irregulares tenemos que sabernos la segunda columna de la lista. OJO: No hace falta poner la -ed a work ni tampoco poner la segunda columna de drink (o sea, drank) porque la marca de pasado ya está en el didn’t!! Yes, I did / No, I didn’t Yes, he did / No, he didn’t… OJO: No hace falta poner la -ed a work ni tampoco poner la segunda columna de drink (o sea, drank) porque la marca de pasado ya está en el Did. b) Si las tres últimas letras del verbo siguen el esquema: consonante + vocal + consonante Ejemplos: Stop = 1 sílaba + CVC = Stopped Shop = 1 sílaba + CVC = Shopped PAST CONTINUOUS USOS: - Acciones pasadas que tuvieron una larga duración: I was studying for 4 hours. = Yo estuve estudiando durante 4 horas. - Acción pasada larga que es interrumpida por una acción corta: My mother phoned while we were watching TV. = Mi madre llamó mientras estábamos viendo la televisión. - Dos acciones pasadas que estaban ocurriendo al mismo tiempo, a la vez, simultáneamente: We were reading while my parents were cooking. = Nosotros estábamos leyendo mientras mis padres estaban cocinando. PALABRAS CLAVE: while…, at that moment…, at 5 o’clock… (con horas concretas) Affirmative Negative Interrogative REMEMBER: Subject + Was / Were + -ING I was working (Yo estaba trabajando) You were working (Tú estabas trabajando) He was working She was working It was working We were working You were working They were working Subject + Was / were + -ING I was not working (Yo no estaba trabajando) You were not working (Tú no estabas trabajando) He was not working She was not working It was not working We were not working You were not working They were not working REMEMBER: was not = wasn’t were not = weren’t Was / Were+ Subject + -ING? Was I working? (¿Estaba yo trabajando?) Were you working? (¿Estabas tú trabajando…?) Was he working? Was she working? Was it working? Were we working? Were you working? Were they working? Respuesta corta: Yes, I was / No, I was not Yes, you were / No, you were not * LOS DOS ZAPATOS: Was / Were + Verbo en ING * Cuando añadimos el sufijo –ing a verbos terminados en –y, nunca quitamos la –y. Ejemplos: Playing y Studying (pero nunca plaing o studing) * La consonante final del verbo se dobla cuando: a) El verbo sólo tiene una sílaba b) Si las tres últimas letras del verbo siguen el esquema: consonante + vocal + consonante Swim = 1 sílaba + CVC = swimming WILL + INFINITIVO (FUTURO SIMPLE) USOS: - Predicciones sin evidencia y/o deseos sobre el futuro: I will be rich in the future (Yo seré rico en el futuro) / We will travel to Miami one day. (Nosotros viajaremos a Miami algún día) = Se traduce por Futuro Simple (comeré, viviré, compraré…) PALABRAS CLAVE: - soon, tomorrow, next month, in a year, I think, I don’t think, maybe, perhaps… Affirmative Negative Interrogative REMEMBER: Subject + Will not or Will + Subject + Infinitive…? * Todas las personas se I will buy Won’t + Infinitive conjugan igual. * Recuerda que son Will I buy…? = ¿Compraré…? (Yo compraré) I will not buy predicciones sin Will you buy…?= ¿Comprarás…? You will buy evidencia, sin prueba. Es (Yo no compraré) decir, son cosas que Will he buy…?= ¿Comprará él…? You will not buy (Tú comprarás) decimos sin ningún tipo (Tú no comprarás) Will she buy?=¿Comprará ella…? He/she/it will buy de base o prueba. He/she/it will not buy He thinks he will win Will it buy…? We will buy We will not buy the race Will we buy…? You will not buy You will buy = Él cree que ganará la carrera Will you buy…? They will not buy They will buy (Lo dice porque es lo Will they buy…? OJO: ¡TODAS LAS que desea, es su opinión, OJO: Respuesta corta: WILL NOT = WON’T pero no es una PERSONAS SE Yes, I will / No, I will not / Yes, she I will not go = Yo no iré predicción basada en CONJUGAN IGUAL! will / No, she will not… I won’t go = Yo no iré evidencias) BE GOING TO + INFINITIVO USOS: - Planes de futuro no del todo cerrados o intenciones. I am going to buy a new car = Me voy a comprar un coche nuevo / Tengo la intención de comprarme un coche nuevo. // She is going to do her homework = Va a hacer sus deberes… - Predicciones con evidencia que hacemos sobre lo que podemos ver en el momento, es decir, me baso en lo que veo para hacer la predicción = The sky is dark. It is going to rain! = El cielo está oscuro. ¡Va a llover! // That woman is pregnant. She is going to have a baby = Esa mujer está embarazada. Va a tener un bebé. PALABRAS CLAVE: - soon, tomorrow, next week, in a month… Affirmative Negative Interrogative REMEMBER: * Se suele traducir como “Ir a…” o “Tener la Subject + Am / Is / Are + Subject + Am / Is / Are + Am / Is / Are + Subject + Going intención de…” o “Tener Going To + Infinitive Not + Going to + Infinitive to + Infinitive? planeado…” I am going to travel I am not going to travel Am I going to travel? (Yo voy a viajar) (Yo no voy a viajar) (¿Voy a viajar…?) You are going to travel You are not going to travel Are you going to travel? (Tú vas a viajar) (Tú no vas a viajar) (¿Vas a viajar…?) He is going to travel He is not going to travel Is he going to travel? She is going to travel She is not going to travel Is she going to travel? It is going to travel It is not going to travel Is it going to travel? We are going to travel You are going to travel They are going to travel OJO! No te olvides de conjugar el verbo To Be e incluir en infinitivo al final: We are going to play. We are not going to travel You are not going to travel They are not going to travel Are we going to travel? Are you going to travel? Are they going to travel? Respuesta corta: Yes, I am / No, I am not Yes, you are / No, you aren’t Yes, he is / No, he isn’t … * Cuando añadimos el sufijo –ing a verbos terminados en –y, nunca quitamos la –y. Ejemplos: Playing y Studying (pero nunca plaing o studing) * La consonante final del verbo se dobla cuando: a) El verbo sólo tiene una sílaba b) Si las tres últimas letras del verbo siguen el esquema: consonante + vocal + consonante Ejemplos: Swim = 1 sílaba + CVC = swimming Shop = 1 sílaba + CVC = Shopping