- INGLES_UNI_13_CAS
Anuncio

Educación secundaria
Dirección Xeral de Educación, Formación
para personas adultas
Profesional e Innovación Educativa
Ámbito de comunicación
Lengua inglesa
Educación a distancia semipresencial
Módulo 4
Anexo gramatical 13
Página 1 de 46
Índice
1.
Introducción...............................................................................................................3
1.1
2.
Descripción del anexo gramatical ................................................................................. 3
Secuencia de contenidos y actividades ..................................................................4
2.1
Presente simple ............................................................................................................ 4
2.1.1
2.1.2
2.1.3
2.1.4
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
Genitivo sajón............................................................................................................. 13
Demostrativos: this / that, these / those ...................................................................... 14
Presente continuo....................................................................................................... 15
Distinción entre el presente simple y el continuo......................................................... 18
Wh-questions.............................................................................................................. 21
2.6.1
2.6.2
2.6.3
2.7
Verbo to be.........................................................................................................................................................4
Verbo have got ...................................................................................................................................................6
There is / there are.............................................................................................................................................7
El resto de los verbos.........................................................................................................................................9
Partículas interrogativas (Wh-words) ...............................................................................................................21
Wh-questions en el presente simple ................................................................................................................22
Wh-questions en el presente continuo .............................................................................................................25
La expresión del tiempo.............................................................................................. 26
2.7.1
2.7.2
2.7.3
La hora .............................................................................................................................................................26
La fecha............................................................................................................................................................27
Preposiciones de tempo (at / in / on)................................................................................................................29
2.8 Comprensión escrita................................................................................................... 30
2.9 Actividades de autoevaluación.................................................................................... 31
2.10 Vocabulario básico de la unidad ................................................................................. 33
2.10.1 La expresión del tiempo ...................................................................................................................................38
2.11 Soluciones de las actividades ..................................................................................... 39
Página 2 de 46
1.
Introducción
1.1
Descripción del anexo gramatical
Este anexo gramatical se dedica a revisar contenidos abordados previamente en los anexos
9 y 10. Concretamente, revisaremos los siguientes contenidos:
Los presentes simple y continuo de los verbos.
La distinción entre el presente simple y el presente continuo.
Los demostrativos.
El genitivo sajón.
Las preguntas con las partículas interrogativas (wh-questions).
Los meses, los días, las fechas y las horas.
Del mismo modo, trataremos el siguiente vocabulario:
Información personal.
Lugares de la casa.
Lugares en la ciudad y en el campo.
Actividades cotidianas y de recreo.
Deportes.
Ropa y accesorios.
Expresión del tiempo.
Página 3 de 46
2.
Secuencia de contenidos y actividades
2.1
Presente simple
2.1.1 Verbo to be
To be (ser o estar)
Frases afirmativas
Frases negativas
Preguntas
Respuestas cortas (+/-)
I am
(I’m)
Soy/estoy
I am not
(I’m not)
No soy/no estoy
Am I?
¿Soy/estoy?
Yes, you are.
No, you aren’t.
Sí
No.
You are
(You’re)
Eres/estás
You are not
(You aren’t)
No eres/no
estás
Are you?
¿Eres/estás?
Yes, I am.
No, I’m not.
Sí
No.
He is
(He’s)
Es/está
He is not
(He isn’t)
No es/no está
Is he?
¿Es/está?
Yes, he is.
No, he isn’t.
Sí
No.
We are
(We’re)
Somos/
estamos
We are not
(We aren’t)
No somos/
no estamos
Are we?
¿Somos/
estamos?
Yes, you are.
No, you aren’t.
Sí.
No.
You are
(You’re)
Sois/
estáis
You are not
(You aren’t)
No sois/
no estáis
Are you?
¿Sois/
estáis?
Yes, we are.
No, we aren’t.
Sí.
No.
They are
(They’re)
Son/están
They are not
(They aren’t)
No son/
no están
Are they?
¿Son/están?
Yes, they are.
No, they aren’t.
Sí.
No.
En resumen:
Forma afirmativa: sujeto + am ('m) / are ('re) / is ('s)
Forma negativa: sujeto + 'm not / aren't / isn't
Forma interrogativa: am / are / is + sujeto?
Respuesta corta:
– Afirmativa: Yes, sujeto + am / are / is (en la respuesta corta afirmativa no podemos
emplear la forma contraída).
– Negativa: No, sujeto + 'm not / aren't / isn't (en la respuesta corta negativa empleamos la forma contraída).
El verbo to be significa ser o estar, pero también puede significar:
Tener años (to be years old), tener hambre o sed (to be hungry/thirsty), tener miedo (to
be scared/afraid)...
– I'm 30 years old (tengo 30
anos)
Hacer frío – calor (to be cold – hot).
– I'm scared of dogs (tengo miedo de los perros).
– It's cold in here (hace frío aquí).
Página 4 de 46
Actividades propuestas
S1.
Observe el perfil de Shakira y complete su perfil con su propia información. Después, complete las oraciones con la forma adecuada del verbo to be.
1. [_______] (Shakira / be) single? Yes, [_______].
2. [_______] (Shakira / not / be) a man.
3. [_______] (Ricky Martin and Gerard Piqué / be) her friends.
4. [_______] (Twilight and True Blood / be) her favourite books? No, [______]
5. [_______] (you / be) a woman? Yes / No, [_______]
6. [_______] (you / be) single? Yes / No, [_______]
7. [_______] [I / (not) be] from the USA.
8. [_______] [my favourite books (not) be] The Da Vinci Code and Angels and
Demons.
Página 5 de 46
2.1.2 Verbo have got
Have got (tener)
Frases afirmativas
I have got
(I’ve got)
Tengo
You have got
(You’ve got)
Tienes
He has got
(He’s got)
Tiene
We have got
(We’ve got)
Tenemos
You have got
(You’ve got)
Tenéis
They have got
(They’ve got)
Tienen
Frases negativas
I have not got
(I haven’t got)
You have not
got
(You haven’t
He has not got
(He hasn’t got)
We have not got
(We haven’t got)
You have not
got (You haven’t
got)
They have not
got (They haven’t got)
Preguntas
Respuestas cortas (+/-)
No tengo
Have I got?
¿Tengo?
No tienes
Have you got?
¿Tienes?
No tiene
Has he got?
¿Tiene?
No tenemos
Have we got?
¿Tenemos?
No tenéis
Have you?
¿Tenéis?
No tienen
Have they got?
¿Tienen?
Yes, you have
No, you haven’t
Yes, I have
No, I haven’t
Sí.
No.
Yes, he has
No, he hasn’t
Sí.
No.
Yes, you have
No, you haven’t
Yes, we have
No, we haven’t
Sí.
No.
Yes, they have
No, they haven’t
Sí.
No.
Sí.
No.
Sí.
No.
En resumen:
Forma afirmativa: sujeto + have ('ve) / has ('s) + got.
Forma negativa: sujeto + haven't / hasn't + got.
Forma interrogativa: have / has + sujeto + got?
Respuesta corta (sin got):
– Afirmativa: Yes, sujeto + have / has (en la respuesta corta afirmativa no podemos
emplear la forma contraída)
– Negativa: No, sujeto + haven't / hasn't (en la respuesta corta negativa empleamos la
forma contraída).
Actividades previstas
S2.
Complete las oraciones con el nombre de las habitaciones y con la forma correcta del verbo have got.
Celebrity homes
1. We are Melanie and Antonio and
this is our ...
2. He is Jamie Oliver, the famous
English cook and this is his...
Página 6 de 46
3. They are Lewis Hamilton, the
famous F1 pilot, and his girlfriend.
This is their ...
a) [_____] a big wardrobe but [_____]
any curtains.
b) [_____] a carpet? Yes / no, [_____].
a) [_____] a white fridge but
[_____] a dishwasher.
b) [_____] a microwave? Yes / no,
[_____].
a) [_____] a bath but [_____] a blue
washbasin.
b) [_____] a mirror? Yes / no,
[_____].
2.1.3 There is / there are
There is / there are (hay)
Frases afirmativas
Frases negativas
Preguntas
There is + singular
Ej: There is a park in my
village.
Hay un parque en mi pueblo.
There isn’t + singular
Ej: There isn’t a park in my
village.
No hay ningún parque en mi
pueblo.
Is there + singular?
Ej: Is there a park in your
village?
¿Hay un parque en tu pueblo?
There are + plural
Ej: There aren’t any parks near
my flat.
No hay ningún parque cerca de
mi piso.
Are there + plural?
Ej: Are there any parks near
your flat?
¿Hay parques cerca de tu
piso?
There are + plural
Ej: There are two parks near
my flat.
Hay dos parques cerca de mi
piso.
Respuestas cortas (+/-)
Yes, there is
No, there isn’t
Yes, there are
No, there aren’t
¡Recuerde! Use any en negativas e interrogativas con there are
En resumen:
Forma afirmativa: there is (‘s) + singular / there are + plural
Forma negativa: there isn't + singular / there aren't + plural
Forma interrogativa: is there + singular / are there + plural?
Respuesta corta:
– Afirmativa: Yes, there is / there are (en la respuesta corta afirmativa no podemos
emplear la forma contraída).
– Negativa: No, there isn't / there aren't (en la respuesta corta negativa empleamos la
forma contraída).
Página 7 de 46
Actividad propuesta
S3.
Observe el mapa de la ciudad y complete con la forma correcta de there is / there are.
1. [_______] two banks in the city? Yes / no, [_______].
2. [_______] a lake in the park.
3. [_______] a sports centre opposite the church.
4. [_______] a chemist's in the city? Yes / no, [_______].
5. [_______] two bridges in the park, [_______] only one.
6. [_______] four trees in the park.
Página 8 de 46
2.1.4 El resto de los verbos
Presente simple - Resto de verbos
Frases afirmativas
Frases negativas
Preguntas
I play
Juego
I don’t play
No juego
Do I play?
¿Juego?
You play
Juegas
You don’t play
No juegas
Do you play?
¿Juegas?
He/she/it plays
Juega
He/she/it doesn’t play
No juega
¿Juega?
We play
Jugamos
We don’t play
No jugamos
Does he/she/it
play?
Do we play?
¿Jugamos?
You play
Jugáis
You don’t play
No jugáis
Do you play?
¿Jugáis?
They play
Juegan
They don’t play
No juegan
Do they play?
¿Juegan?
Respuestas cortas
Afirmativas
Yes, I / you / we / they do
Yes, he / she / it does
3ª persona del singular - Forma afirmativa
Negativas
Normalmente añadimos –s al verbo para formar a 3ª persona
del singular (he, she, it). Ej.: I drink – he drinks
No, I / you / we / they don’t
No, he / she / it doesn’t
Pero...
Añadimos –es a los verbos acabados en -ss, -sh, -ch, -x, -o.
Ej.: I watch – he watches.
Con los verbos terminados en consonante + y, cambiamos la –
y por –ies.
Ej.: I cry – he cries.
Con los verbos terminados en vocal + y, solo añadimos –s.
Ej.: I play – he plays.
Uso
Hábitos y acciones regulares. Ej.: He visits his friends every Sunday.
Verbos estáticos. Ej.: Do you like fish?
Expresiones empleadas con el presente simple
Frequency adverbs: always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, never.
Time expressions: every day / week / Friday…, on Mondays / Sundays…, at the weekend…, in the morning / afternoon…, in
winter / spring…, once a day / week…
En resumen:
Forma afirmativa: sujeto + infinitivo / infinitivo + s (he/she/it)
Forma negativa: sujeto + don't / doesn't + infinitivo
Forma interrogativa: do / does + sujeto + infinitivo?
Respuesta corta (en la respuesta corta no empleamos el verbo, sino el auxiliar do/does):
– Afirmativa: Yes, sujeto + do / does
– Negativa: No, sujeto + don't / doesn't
Página 9 de 46
Actividades propuestas
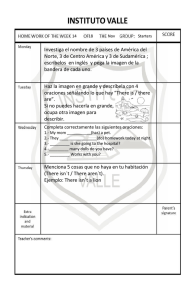
S4.
Mire las siguientes imágenes sobre las rutinas de Jennifer y complete con el verbo que corresponda. Emplee la tercera persona del singular del presente simple.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
Jennifer [_______] (1) at quarter to eight in the morning but she [_______] (negative)
(2) until eight o'clock. Then she [_______] (3) in the bathroom. On Sundays she usually
[_______] (4) instead. After that, she [_______] (5).
At half past eight she [______] (6) with her family. She usually has cereal for
lunch. At 9.00 Jennifer takes her car and [_______] (7) because she s[______] (8)
at 9.30. Then, she [______] (9) at one o'clock. When she [______] (10) in the afternoon…
When she [______] (10) in the afternoon, she [______] (11). At 19.00 when she
[_______] (12), Jennifer [_______] (13). Then, she [______] (14) with her family.
At night she [_______] (15) with her friends. Her favourite TV show is Lost.
Página 10 de 46
Sometimes she [_______] (16). Before she [_______] (17) she [_______] (18).
But at the weekend she normally [_______] (19) or [_______] (20) with her
friends.
Observe las imágenes y diga las actividades que hace y las que no hace cada
persona. Emplee el presente simple.
Free time activities
S5.
S6.
1. He plays volleyball but
2. We [_________] but we
3. They [_________] but
4. She [_________] but
he doesn't ...
[_________]
they [_________]
she [_________]
Observe el cuadro y haga preguntas y respuestas como en el ejemplo. Emplee
el presente simple.
Laura
1. Paul and Bill
2. You
3. Ernest
Ejemplo: Does Laura play tennis? No, she doesn't. She goes dancing.
1. [______________________]?
Yes, they do.
2. [______________________]? (you / cook)
[____________]
3. [______________________]? (Ernest / play hockey) [____________]
S7.
Complete las oraciones con el presente simple del verbo entre paréntesis.
1. [_______] (you / cook) eggs in the microwave? Yes, [_______].
2. [_______] (there is /are) ten shopping centres in your city? No, [_______].
3. [_______] (Anna / have got) any hobbies? Yes, [_______].
4. [_______] (I / not go) to school in the evening.
Página 11 de 46
5. [_______] (Nicolas Sarkozy / be) French? Yes, [_______].
6. [_______] (my grandmother / not watch) TV every day.
7. [_______] (my cat / sleep) twenty hours a day.
8. [_______] (my neighbours / have got) two new cars. [_______] (they / be)
really expensive.
9. [_______] (people from China / speak) Chinese.
10. [_______] (Andrew and I / work) in an office.
Página 12 de 46
2.2
Genitivo sajón
Genitivo sajón - Possessive 's
Cuándo
Para expresar posesión tenemos dos formas:
Preposición “of” (cuando el poseedor no es una persona). Ej.: The window of my house (la ventana de mi
casa).
Genitivo sajón (cuando el poseedor es una persona). Ej.: My brother’s daughter (la hija de mi hermano).
Cómo
Poseedor ‘s + cosa poeída
Paul’s
The man's
My sister's
grandmother
house
boyfriend
(la abuela de Paul)
(la casa del hombre)
(el novio de mi hermana)
*Si el poseedor acaba en –s: poseedor ‘ + cosa poseída. Ej.: the boys’ parents (los padres de los niños).
Actividades propuestas
S8.
Diga a quién pertenece cada pieza de ropa. Emplee el genitivo sajón e it's o
they're.
Pamela Anderson
Steve Urkel
Letizia Ortiz
Ej: It's Pamela's swimming costume.
Página 13 de 46
Lady Gaga
Michael Jackson
2.3
Demostrativos: this / that, these / those
Singular
Plural
Cerca
This
Este/ esta/ esto
These
Estos/ estas
Lejos
That
Ese/ esa/ eso
aquel/ aquella/ aquello
Those
Esos/ esas
aquellos/ aquellas
This/ that/these/those pueden ir con un sustantivo o pueden ir solos.
Con sustantivo:
– This house is very beautiful but it is very expensive. (Esta casa es muy bonita pero
es muy cara)
– Who’s that person? He’s my brother. (¿Quién es esa persona? Es mi hermano).
Sin sustantivo:
– This is a very beautiful house but it is very expensive. (Esta es una casa muy bonita
pero es muy cara.)
– Who’s that? (¿Quién es ese?).
Actividades propuestas
S9.
Haga preguntas y respuestas como en el ejemplo. Emplee los demostrativos.
What is this?
It’s a lamp.
1.
What is that?
It’s a desk.
2.
What are these?
They’re chairs.
3.
Página 14 de 46
What are those?
They’re clocks.
4.
2.4
Presente continuo
to be + -ing
Frases afirmativas
Frases negativas
Preguntas
I am
I'm
Yo estoy
jugando
I am not
I'm not
Yo no estoy
jugando
Am I
¿Estoy yo
jugando?
You are You're
Tú estás
jugando
You are not
You aren't
Tú no estás
jugando
Are you
¿Estás tú
jugando?
He is He's
El está jugando
He is not
He isn't
Él no está
jugando
Is he
¿Está él
jugando?
We are We're
Nosotros
estamos
jugando
We are not
We aren't
You are You're
Vosotros
estáis jugando
They are
They're
Ellos están
jugando
playing
playing
Are we
¿Estamos
nosotros
jugando?
You are not
You aren't
Vosotros no
estáis jugando
Are you
¿Estáis
vosotros
jugando?
They are not
They aren't
Ellos no están
jugando
Are they
¿Están ellos
jugando?
Respuestas cortas
Afirmativas
Negativas
Yes, I am
Yes, you/we/they
are
Yes, he/she/it is
No, I'm not
No, you/we/they
aren't
No, he/she/it isn't
playing?
Nosotros no
estamos
jugando
Forma -ing
Por lo general añadimos –ing al verbo para formar el gerundio. Ej: drink – drinking.
Pero
Con los verbos acabados en -y, omitimos la -y y añadimos -ing.
Con los verbos terminados en -ie, cambiamos –ie por –ying. Ej: die - dying.
Con los verbos acabados en sílaba tónica y consonante - vocal - consonante
doblamos la última consonante. Ej: stop – stopping.
Uso
Acciones que están ocurriendo ahora. Ej: What are you doing now? I'm sending a text message to Paul.
– Acciones que están ocurriendo en un tiempo próximo a ahora (acciones temporales). Ej: Kate's really studying hard for her ex-
ams this week.
– Planes futuros. Ej: What are you doing tomorrow night? I'm seeing some friends.
Expresiones empleadas con el presente continuo
Acciones que están ocurriendo ahora: (right) now, at the moment, at present...
– Acciones temporales: this week, this month, today…
– Planes futuros: tomorrow, tonight, next week, next Sunday...
En resumen:
Forma afirmativa: sujeto + am ('m) / are ('re) / is ('s) + -ing
Forma negativa: sujeto + 'm not / aren't / isn't + -ing
Forma interrogativa: am / are / is + sujeto + -ing?
Página 15 de 46
Respuesta corta (en la respuesta corta no usamos la forma –ing):
– Afirmativa: Yes, sujeto + am / are / is (en la respuesta corta afirmativa no podemos
emplear la forma contraída).
– Negativa: No, sujeto + 'm not / aren't / isn't (en la respuesta corta negativa empleamos la forma contraída).
Actividades propuestas
S10.
Observe la ilustración. A continuación, complete las oraciones con la forma afirmativa o negativa de los verbos entre paréntesis.
1. Kate [_______________] (wear) jeans.
2. Kate [_______________] (hold) Jack's hand.
3. Jack and Sawyer [_______________] (wear) trousers.
4. Jack and Sawyer [_______________] (run).
5. I [_______________] (wear) a white T-shirt.
6. I [_______________] (sit) in a chair.
Lost
S11.
Complete con la forma interrogativa y la respuesta corta del verbo adecuado.
Two different holidays
Brad and Angelina are angry with each other. This week Angelina is spending her holidays in
Hawaii while Brad is staying at home with their children. This is what they are doing today.
Time
8.00 h
11.30 h
18.00 h
23.00 h
Angelina
Brad
Ej.: Are they having breakfast? No, they aren't.
1. [____] she [________]?
Página 16 de 46
Yes, she is.
18.00
2. [____] he [________]? (have a shower)
[________]
18.00
3. [____] he [________]?
Yes, he is.
11.30
4. [____] she [________]? (do yoga)
[________]
11.30
5. [____] they [________]? (think about each other) [________]
23.00
6. [____] he ____________?
8.00
Página 17 de 46
Yes, he is.
2.5
Distinción entre el presente simple y el continuo
Presente simple
Presente continuo
Hábitos y acciones regulares.
Acciones que están ocurriendo agora.
Ej: He visits his friends every Sunday (Visita a sus amigos
todos los domingos).
Ej: What are you doing now? (¿Qué estás haciendo ahora?)
– Expresiones típicas:
– Expresiones típicas:
– (Right) now [ahora (mismo)].
– Adverbios de frecuencia [always (siempre), usually
–
–
–
–
–
(normalmente), often (a menudo), sometimes (a
veces), never (nunca)…].
Every day / week... (todos los días / semanas…).
On Mondays / Tuesdays… (los lunes / martes…).
In the morning / in the afternoon / at night… (por la
mañana / por la noche)…
In winter / in autumn (en el inverno / en el otoño…).
Once a week / twice a day / three times a month...
(una vez a la semana / dos veces al día / tres veces al mes…).
– At the moment (en este momento).
– At present (en el presente, ahora).
– Look! / Listen! (¡Mire! / ¡Escuche!)
Acciones que están ocurriendo en un tiempo próximo a
ahora (acciones temporales).
Ej: Kate's really studying hard for her exams this week. (Kate realmente está estudiando mucho para sus exámenes
esta semana)
– Expresiones típicas:
– This week/month/summer… (esta semana, este
mes, este verano…).
– Today (hoy).
Verbos estáticos (nunca en tiempos continuos). Expresan
Plans nun futuro próximo.
sentimientos y procesos mentales.
Ej: Do you like fish? (¿Te gusta el pescado?)
Ej: Tonight I'm going to the cinema with some friends.
(Esta noche voy al cine con unos amigos)
– Like (gustar), love (encantar), hate (odiar), prefer (prefe-
rir), want (querer)…
– Remember (recordar), forget (olvidar), think (pensar), understand (entender), know (saber)…
– Expresiones típicas
– Tomorrow (mañana).
– Tonight (esta noche).
– Next week/next Sunday... (la próxima semana, el
próximo domingo...).
Actividades propuestas
S12.
Coloque las siguientes oraciones en el cuadro según el tiempo verbal y el significado.
1. Please be quiet! This is a library and people are studying.
2. What do you usually do at the weekend?
3. What is he doing at the moment? He's making dinner.
4. It often rains in December.
5. My brother goes to the gym twice a week.
6. I'm going to my aunt's house this weekend.
7. They're redecorating their house this week.
8. Do you know that girl? Yes, but I don't remember her name.
9. Mike's having a party tomorrow.
10. Do you hate doing your homework?
Página 18 de 46
– Hábitos. Acciones regulares
Presente simple
– Verbos estáticos
– Acciones que ocurren ahora
Presente continuo
– Acciones temporales
– Planes futuros
S13.
Coloque las siguientes expresiones temporales debajo del tiempo verbal que le
corresponda.
every year - at the moment - today - right now - twice a month - tomorrow - never
- once a week - on Sundays - twice a day - every morning - rarely - this month
Presente simple
S14.
Presente continuo
Escoja la respuesta adecuada.
1. Julia isn't at home at the moment. She visits / she's visiting some friends.
2. What time do you usually have / are you usually having breakfast?
3. How often do the Simpsons go / are the Simpsons going on holiday?
4. Rafael Nadal is a tennis player. He plays / he's playing every day.
5. Why are you under the table? What do you do / are you doing?
6. Martin doesn't like / isn't liking tea. He prefers / he's preferring coffee.
S15.
Complete las oraciones con el presente simple o con el presente continuo del
verbo entre paréntesis.
1. [______________] (my sister / not / usually / go) to work by car, but this
week [______________] (she / drive) to work.
2. What's the meaning of "pencil"? [______________] (I / not / know).
3. [______________] (I / live) in the USA, but this year [______________] (I /
live) in Spain because [______________] (I / want) to learn Spanish.
4. [______________] (he / take) his cat to the vet tomorrow?
5. What [______________] (Mary / usually / do) after school?
[______________] (she / sometimes / go) for a drink with her friends.
6. Don’t forget to take your umbrella. [______________] (it / rain).
Página 19 de 46
7. Jennifer is a good football player but [______________] (she / not / play)
very often.
8. It's a nice day today. [______________] (the sun / shine) and
[______________] (birds / sing).
Página 20 de 46
2.6
Wh-questions
2.6.1 Partículas interrogativas (Wh-words)
Wh-words
What...?
¿Qué / cuál...?
What time...?
¿A qué hora...?
What kind of...?
¿Qué clase de...?
Which...?
¿Cuál...?
Who...?
¿Quién...?
Where...?
¿Dónde...?
When...?
¿Cuándo...?
Why...?
¿Por qué…?
How...?
¿Cómo...?
How often...?
¿Con qué frecuencia…?
How much...?
¿Cuánto/a...?
How many...?
¿Cuántos/as...?
Whose...?
¿De quién...?
Actividades propuestas
S16.
Escriba la partícula interrogativa correcta para cada una de las siguientes preguntas.
1. [____________] do you need?
Some money.
2. [____________] is in the kitchen?
My mother.
3. [____________] do you watch television?
After dinner.
4. [____________] trousers have you got?
Seven.
5. [____________] do you live?
In London.
6. [____________] do you go to school?
At 8 o’clock.
7. [____________] are you a singer?
Because I love music.
8. [____________] milk do you need?
One glass.
9. [____________] music do you like?
Pop music.
10. [___________] do you use your computer?
Every day.
Página 21 de 46
2.6.2 Wh-questions en el presente simple
Su estructura es: partícula interrogativa + forma interrogativa del verbo:
What is your address?
Where have you got your CDs?
How many parks are there in your town?
When do you start classes?
Why do you go to the gym every day?
Wh-questions en el present simple
Pronombre interrogativo
…?
Verbo en forma interrogativa
Wh-word
Am / is / are
Sujeto
What
is
your name?
Wh-word
have / has
Sujeto
got
How many brothers and sisters
have
you
got?
...?
...?
Wh-word
is / are
there
...?
How much milk
is
there
in the fridge?
Wh-word
do / does
Sujeto
Infinitivo
Where
do
you
work?
What time
does
your sister
get up
...?
in the morning?
*Who y what pueden actuar como sujeto de la oración. En ese caso, la estructura de la
pregunta será partícula interrogativa + verbo en la forma afirmativa.
What happens?
Compare:
Who loves Romeo? Juliet (sujeto) loves Romeo (¿Quién ama a Romeo? Julieta ama a
Romeo).
Pero...
Who does Romeo love? Romeo loves Juliet (objeto). (¿A quién ama Romeo? Romeo
ama a Julieta).
Página 22 de 46
Actividades propuestas
S17.
Coloque las siguientes oraciones en los huecos en blanco del cuadro de la página anterior.
1. How often does your brother go to the gym?
2. Where are you from?
3. Why do you like Cristiano Ronaldo?
4. How many students are there in your class?
5. How many pets has your son got?
6. Whose is this house?
S18.
Complete las oraciones con el verbo en el presente simple.
To be.
–
1. Who [____________] (Steve and Jack / be)?
–
2. What [____________] (his name / be)?
Have got.
–
3. How many doors [____________] (your car/ have got)?
–
4. What [____________] (you / have got) in your bedroom?
–
5. Where [____________] (she/ have got) her keys?
There is/are.
–
6. How many students [____________] (there is/are) in this class?
–
7. Where [____________] (there is/are) a hospital in this town?
Other verbs.
S19.
–
8. What time [____________] (the banks/ close) in England?
–
9. How often [____________] (he/ go) swimming?
–
10. Why [____________] (you / smoke)?
Observe las ilustraciones y haga preguntas. Emplee el presente simple.
Baby's day
1. [______] (wh-word) does he get
2. [______] (wh-word) ... he...? He
3. [______] (wh-word) ...? His father
up? He gets up at 7 o'clock every
has a shower every morning.
makes breakfast.
day.
Página 23 de 46
4. [______] (wh-word) ... he ...? He
5. [______] (wh-word)... his mot-
6. [______] (wh-word) ... he ...? He
watches TV in the living room.
her ... ? She goes to work by car.
loves cats because they're very
nice.
S20.
Haga preguntas para las siguientes respuestas.
To be.
– 1. The children are on holiday because they're very tired.
–
2. James is at school.
Have got.
– 3. I've got my Britney's CD in a box in my bedroom.
–
4. They've got a lot of milk in their fridge.
There is / are.
– 5. There are twenty students in class.
Rest of verbs.
– 6. I have lunch at 9.00.
–
7. She does yoga because it's very healthy.
–
8. I love Hannah Montana.
Página 24 de 46
2.6.3 Wh-questions en el presente continuo
Su estructura es: partícula interrogativa + forma interrogativa del verbo:
What are you doing at the moment?
Where are you working now?
Wh-questions with present continuous
Pronombre interrogativo
…?
Verbo en forma interrogativa
Wh-word
is / am / are
Sujeto
-ing?
Why
are
you
crying?
...?
Actividades propuestas
S21.
Coloque las siguientes oraciones en el cuadro superior.
1. What is your sister listening to?
2. Where are you going to?
3. Why are you wearing a coat?
S22.
Formule preguntas para las siguientes respuestas.
1. She's doing karate at the moment.
2. I'm watching TV because Big Brother is my favourite programme.
3. We're having breakfast at home.
4. Peter's driving fast.
5. I'm reading a book.
Página 25 de 46
2.7
La expresión del tiempo
2.7.1 La hora
Pregunta
The time (la hora)
What time is it? (¿Qué hora es?)
What’s the time? (¿Qué hora es?)
Resto de horas
It’s + hora + o’clock
It’s twelve o’clock
(Son las doce en punto)
It’s + minutos + past + hora
It’s + minutos + to + hora
Respuesta
En punto
It’s + min + past + hora
It’s five / ten past...
Son las ... y cinco / y diez.
It’s + quarter + past + hora
It’s quarter past...
Son las ... y cuarto.
It’s + min + past + hora
It’s twenty / twenty-five past...
Son las ... y veinte / veinticinco.
It’s + HALF + past + HORA
It’s half past...
Son las ... y media.
It’s + MIN + to + HORA SIGUIENTE
It’s five / ten to...
Son las ... menos cinco / diez
It’s + QUARTER + to + HORA
SIGUIENTE
It’s quarter to...
Son las ... menos cuarto.
Fíjese en que:
Cuando empleamos to decimos los minutos que quedan para la siguiente hora.
– 9.35 It’s twenty-five to ten.
– 9.35 It’s twenty-five to nine.
Tanto a “...y cuarto” como a “...menos cuarto” empleamos “quarter”, no “fifteen”.
– It’s quarter past three.
– It’s fifteen past three.
Página 26 de 46
Actividades propuestas
S23.
Escriba la hora.
a. 4.20
d. 10.45
b. 3.00
y. 8.30
c. 8.50
f. 11.35
2.7.2 La fecha
The date (la fecha)
Pregunta
What’s the date today? (¿Qué fecha es hoy?)
¿Cómo escribimos las fechas?
It is...
It is...
Día
Monday
Número (cardinal/ordinal)
14 / 14th
Mes
December
Respuesta
¿Cómo leemos las fechas?
It is...
It is...
Día
Monday
The + ordinal
The fourteenth
Of + mes
Of December
Números ordinales
1st
first
2nd
second
3rd
third
4th
fourth
5th
fifth
6th
sixth
7th
seventh
8th
eighth
9th
ninth
10th
tenth
11th
eleventh
12th
twelfth
13th
thirteenth
14th
fourteenth
15th
fifteenth
16th
sixteenth
17th
seventeenth
18th
eighteenth
19th
nineteenth
20th
twentieth
21st
twenty-first
22nd
twenty-second
23rd
twenty-third
24th
twenty-fourth
25th
twenty-fifth
26th
twenty-sixth
27th
twenty-seventh
28th
twenty-eighth
29th
twenty-ninth
30th
thirtieth
31st
thirty-first
Fíjese en los siguientes aspectos:
Los ordinales primero, segundo y tercero (y sus compuestos vigésimo primero, trigésimo primero...) son irregulares en inglés: first, second, third, twenty-second, thirtyfirst...
Página 27 de 46
Los demás números añaden -th para formar el ordinal. Algunos números sufren cambios ortográficos:
– five pasa a fifth (y no fiveth).
– eight solo añade -h (eighth y no eightth).
– nine pasa a ninth (y no nineth).
– twelve pasa a twelfth (y no twelveth).
– twenty, thirty... pasan a twentieth, thirtieth... ( y no twentyth, thirtyth).
Actividades propuestas
S24.
Complete el cuadro. Primero, relacione cada celebración con su descripción. A
continuación, escriba las fechas que correspondan a cada festividad.
Celebrations
1. Christmas
– a. US people celebrate their independence from England.
2. Bonfire Night / Guy Fawkes' Night
– b. Sweethearts celebrate this day with presents and love cards.
3. April Fool's Day
– c. Christian people celebrate the birth of Jesus Christ.
4. St Patrick's Day
– d. People play little jokes on their friends and family.
5. Independence Day
– y. Ireland's national day when people wear green clothes.
6. Valentine's Day
– f. British people make Guy figures with old clothes and burn them.
7. Halloween
– g. People wear costumes and say "trick or treat".
Dates
We say
We write
1. 14 February
2. 17 March
3. 1 April
4. 4 July
5. 31 October
6. 5 November
7. 25 December
Página 28 de 46
Event
2.7.3 Preposiciones de tiempo (at / in / on)
At
+ horas: at seven o'clock (a las siete)
+ períodos de vacaciones:
In
+ meses: in May (en mayo)
+ estaciones: in winter (en invierno)
– at Christmas (en Navidad)
+ anos: in 1999 (en el año 1999)
– at Easter (en Pascua)
+ partes del día:
– at the weekend (en el fin de sema-
– in the morning (por la mañana)
na)
– at (mid)night (por la noche, a medianoche)
– at noon (al mediodía)
– in the afternoon (por la tarde)
– in the evening (por la tarde/noche)
– pero at night.
On
+ días:
– on Monday (el lunes)
– on Christmas Day (el día de Navi-
dad)
– on Saturday night (el sábado por la
noche)
– on Sunday morning (el domingo
por la mañana)
+ fechas: on 7th July (el 7 de julio)
No se usa ninguna preposición de tiempo en las expresiones que comiencen por:
This: this morning (esta mañana).
Last: last week (la semana pasada).
Next: next year (el año que viene, el próximo año).
Every: every day (todos los días).
Actividades propuestas
S25.
Complete con at / in / on / .
1. I wake up [______] 7.45.
2. He sometimes works [______] Saturdays.
3. I never go to work [______] the weekend.
4. Families have lunch together [______] Christmas Day.
5. Do you go on holiday [______] August?
6. I'm watching TV [______] this evening.
7. I do my English homework [______] night.
8. I always go out [______] Saturday night.
9. I'm starting a new school year [______] next September.
10. I go skiing [______] winter.
11. The party is [______] the 21st October.
12. Leonard was born [______] 1979.
13. [______] Easter people eat Easter eggs.
14. I get up late [______] Sunday mornings.
Página 29 de 46
2.8
Comprensión escrita
Saint Patrick's Day
Saint Patrick’s Day is the official national holiday of Ireland and is celebrated internationally.
When and where do people celebrate Saint Patrick's Day? People celebrate it on 17th March every year, obviously, in Ireland but also in many
other English-speaking countries like the USA and Australia.
But… who is Saint Patrick? He is the patron saint of Ireland. He was born
in Scotland at the end of the 4th century and died on 17th March. For this
reason, his feast day is celebrated on this day.
It lasts for five days and nights. It usually starts on 13th March and ends
on 17th March with St Patrick’s parade. During the festival, there is music
everywhere. People dress in green, dance and drink green beer. It’s great
fun!
But… why is green so important on St Patrick’s Day? Because it's one of
the colours of the Irish flag and it symbolizes the beginning of spring.
Green is also the colour of the shamrock, one of the special symbols associated with Saint Patrick.
How do people celebrate this day all over the world? On Saint Patrick's Day there are big parades in New York and Boston because
lots of Irish descendants live there. In Chicago you can even find a
green river and in Sidney people eat green hamburgers!! In Dublin, the capital city of Ireland, there is a huge fireworks display in
the evening and fun and games for the kids.
So, next 17th March, why don't you put on some green clothes, pin a
shamrock on your lapel and join in the biggest party in the Irish calendar:
Saint Patrick’s Day!
This Irish man is
wearing a green
jacket, a green hat and
a green and white tie.
He's also carrying a
green umbrella
These girls are smiling
next to a leprechaun,
the traditional elf
This Irish man is
drinking green beer
Actividades propuestas
S26.
Lea el texto y diga si las siguientes afirmaciones son verdaderas o falsas. Si son
falsas, corríjalas.
1. Saint Patrick’s Day is a national feast in Ireland.
2. Saint Patrick's Day is only celebrated in Ireland.
3. Saint Patrick is Irish.
4. Saint Patrick is born on 17th March.
5. The shamrock is one of the symbols associated with Saint Patrick.
6. You can find a green river in Dublin.
Página 30 de 46
2.9
Actividades de autoevaluación
S27.
Complete las oraciones con la forma adecuada del presente simple o del presente continuo.
1. Can you speak more slowly? [________] (I / not / understand).
2. What [_______] (she / do) at the moment? [_______] (she / sit) on the sofa.
3. [________] (I / meet) some friends tomorrow. [________] (you / want) to
come with us?
4. [________] (Molly / usually / empty) the dishwasher at night.
5. What [________] (your brother / do)? He's a doctor.
S28.
Haga preguntas con el presente simple o continuo.
1. There are three dishes in the sink.
2. She gets up at 8.00.
3. She's wearing a coat because it's very cold today.
4. She's got a mirror in the bathroom.
5. I go to work twice a week.
S29.
Escriba las siguientes fechas.
1. Mon. 3 Jan.
2. Wed. 31 Sep.
3. Sat. 12 Oct.
4. Sun. 5 May.
5. Fri. 22 Aug.
S30.
Complete con at / in / on / .
1. Jane is arriving [___] January 26 [___] 2 o'clock [___] the afternoon.
2. It snows here [___] every year [___] December. We always go outside and
play in the snow [___] Christmas day.
3. Michael is leaving [___] Friday [___] noon.
4. Do you usually go to bed very late [___] night?
5. My family normally goes to mass [___] Sunday morning.
S31.
Escoja la respuesta correcta.
1. What time is it? It's ten to five.
a. 4.50
b. 9.55
c. 100.5
Página 31 de 46
2. What's the time? It's quarter past three.
a. 3.45
b. 2.45
c. 3.15
3. [___] elephants are sleeping under the shade of [___] tree.
a. these - those
b. that - that
c. those - that
b. Paul's friends
c. Paul friends
b. my name's wife
c. my wife name
4. [___] are leaving.
a. the Paul's friends
5. Sarah is [___].
a. my wife's name
Página 32 de 46
2.10 Vocabulario básico de la unidad
Información personal
Questions (Preguntas)
First name
Last name
Surname
Spelling of a word
Age
– What is your name?
Answers (Respuestas)
– My name is…
¿Cómo te llamas?
– What is your surname / last name?
Me llamo...
– My surname / last name is…
¿Cómo te apellidas?
– How do you spell it?
Me apellido...
– It's…
¿Cómo se deletrea eso?
– How old are you?
Es…
– I’m... (years old).
¿Cuántos años tienes?
Tengo... años.
– Yes, I am. / Sí.
Marital status
– Are you married?
ted...
No. Estoy soltero, divorciado, separado...
– What nationality are you?
– What is your nationality?
Nationality
Address
Postcode
Phone number
¿Cuál es tu nacionalidad?
– Where are you from?
¿De dónde eres?
– What's your address?
¿Cuál es tu dirección?
– What's your postcode?
¿Cuál es tu código postal?
– What is your mobile / phone number?
¿Cuál es tu número de teléfono / móvil?
– What's your e-mail address?
E-mail address
Job
– No, I'm not. I'm single / divorced / separa-
¿Estás casado?
¿Cuál es tu dirección de correo electrónico?
– What do you do? / What's your job?
¿En qué trabajas? ¿Cuál es tu trabajo?
Página 33 de 46
– I’m Spanish/ English / French / ...
Soy español / inglés /...
– I’m from Spain / England / ...
Soy de España, de Inglaterra,...
–
My address is… 34, Red Hill Avenue.
Mi dirección es Avenida Red Hill, nº 34.
– My postcode is…
Mi código postal es...
– My mobile / phone number is…
Mi número de teléfono / móvil es…
– My e-mail address is…
Mi dirección de correo electrónico es…
– I'm a/an… student
Soy… estudiante
Tenga en cuenta los siguientes aspectos:
En inglés usamos los siguientes títulos o tratamientos. Fíjese que podemos decir: Mr.
Tom Cruise o Mr. Cruise, pero no Mr. Tom.
– Mr. Para hombres (Sr.).
– Mrs. Para mujeres casadas (Sra.).
– Miss. Para mujeres solteiras (Srta.).
– Ms. Para mujeres (sin especificar estado civil).
Para decir nuestra edad no empleamos el verbo have got, sino el verbo to be.
– How old are you? I'm 20 (years old).
– How old have you got? I've got 20 (years old).
Para hablar de nuestra nacionalidad podemos emplear:
– Verbo to be + nacionalidad (Spanish, German, Russian...). Ej.: I'm German.
– Verbo to be + from + país (Spain, Germany, Russia...). Ej.: I'm from Germany.
Las direcciones en inglés siguen este orden:
– Number + name + street (calle) / avenue (avenida) / square (plaza) / road (calle) ...
+ City / Town / Village
– My address is 35, Madison Avenue, New York.
Para leer direcciones y páginas web, debemos emplear este vocabulario:
(dot), @ (at), / (forward slash), \ (backward slash), _ (underscore), – (hyphen)
Para hablar de nuestra profesión en inglés, a diferencia de lo que ocurre en castellano,
tenemos que emplear el artículo a / an.
– I'm an actrees. I'm actress.
– I'm a teacher.
I'm teacher.
La casa
In the kitchen (en la cocina)
English
In the bedroom (en el dormitorio)
Castellano
English
Castellano
a chair
– silla
an alarm clock
– reloj despertador
a cupboard
– armario de la cocina
a bed
– cama
a dishwasher
– lavavajillas
a bedside table
– mesilla de noche
a fridge
– nevera
blinds
– persiana
a microwave
– microondas
curtains
– cortinas
a sink
– fregadero
a cushion
– cojín
a table
– mesa
a picture
– cuadro, foto
a toaster
– tostadora
a wardrobe
– armario
a washing machine
– lavadora
Página 34 de 46
In the bathroom (en el baño)
English
In the living room (en el salón)
Castellano
English
Castellano
a bath
– bañera
an armchair
– silla de brazos
a mirror
– espejo
a carpet
– alfombra
a shower
– ducha
a lamp
– lámpara
a toilet
– váter
a plant
– planta
a washbasin
– lavabo
a shelf
– estante
a sofa
– sofá
Lugares en la cidad y en el campo
Buildings (edificios)
English
Basic needs (necesidades básicas)
Castellano
English
Castellano
an art gallery
– galería de arte
a bank
– banco
a bed and breakfast
– pensión con desayuno
a bar
– bar
a castle
– castillo
a café
– cafetería
a church
– iglesia
a chemist’s / pharmacy
– farmacia
a cinema
– cine
a department store
– grandes almacenes
a hotel
– hotel
a market
– mercado
a house
– casa
a pub
– bar, pub
a library
– biblioteca
a shop
– tienda
a mosque
– mezquita
a shopping centre
– centro comercial
a museum
– museo
a supermarket
– supermercado
a theatre
– teatro
On the town (por la ciudad)
English
Services (servicios)
Castellano
English
Castellano
a bridge
– puente
a hospital
– hospital
a park
– parque
a police station
– comisaría de policía
a pedestrian crossing
– paso de peatones
a post office
– oficina de correos
a river
– río
a school
– escuela
a road
– carretera
a sports centre
– gimnasio
the sea
– mar
a town hall
– ayuntamiento
a square
– plaza
a university
– universidad
a street
– calle
Transport (transporte)
English
In the countryside (en el campo)
Castellano
English
Castellano
an airport
– aeropuerto
a beach
– playa
a bus station
– estación de autobuses
a lake
– lago
a railway / train station
– estación de ferrocarril
a mountain
– montaña
a travel agent’s
– agencia de viajes
a hiking route
– ruta de senderismo
a waterfall
– cascada
Página 35 de 46
Actividades cotidianas
Daily routine (actividades cotidianas)
English
Castellano
English
Castellano
to do the shopping
– hacer la compra
to have dinner
– cenar
to finish work / classes
– acabar el trabajo / clases
to have lunch
– comer
to get dressed
– vestirse
to leave home
– salir de casa
to get home
– llegar a casa
to sleep
– dormir
to get up
– levantarse
to start work / classes
to go to bed
– ir a la cama
to study
– estudiar
to go to work / school
– ir al trabajo / al colegio
to wake up
– despertarse
to have a shower / a bath
– ducharse / bañarse
to work
– trabajar
to have breakfast
– desayunar
– comenzar el trabajo/ las
clases
Actividades de recreo
Hobbies (actividades de recreo)
English
Castellano
English
Castellano
to cook
– cocinar
to listen to music
to do sport
– hacer deporte
to phone friends/family
to go dancing
– ir a bailar
to play the piano/guitar
– tocar el piano / la guitarra
to go for a drink
– salir a tomar unas copas
to read a book/magazine
– leer un libro / una revista
to go out
– salir
to read the newspaper
– leer el periódico
to go shopping
– ir de compras
to stay in
– quedar en casa
to go to a restaurant
– ir al restaurante
to visit friends/family
to go to the cinema
– ir al cine
to watch TV
to have a coffee with
– tomar un café con los
friends
– escuchar música
– llamar a los amigos/a la
familia
– visitar a los amigos/ a la
familia
– ver la televisión
amigos
Deportes
Play... (jugar a...)
English
Go... (ir a …)
Castellano
English
Castellano
basketball
– baloncesto
fishing
– ir de pesca
football
– fútbol
jogging
– correr
golf
– golf
sailing
– navegar a vela
hockey
– hockey
(water) skiing
– hacer esquí (acuático)
rugby
– rugby
swimming
– nadar
table tennis
– ping-pong, tenis de mesa
tennis
– tenis
judo
– yudo
volleyball
– voleibol
karate
– kárate
Do... (hacer...)
Página 36 de 46
Ropa y accesorios
Footwear (calzado)
English
Outerwear (ropa de abrigo)
Castellano
English
Castellano
boots
– botas
an anorak
– anorak
high heels
– tacones
a blazer
– chaqueta americana
sandals
– sandalias
a coat
– abrigo
shoes
– zapatos
a jacket
– cazadora, chaqueta
thongs / flip flops
– chancletas
a raincoat
– impermeable, gabardina
trainers
– deportivos
Dresses, skirts... (vestidos, saias...)
English
Castellano
English
Castellano
a dress
– vestido
a blouse
– blusa
jeans
– vaqueros
a cardigan
– chaqueta de punto
a mini-skirt
– minifalda
a jersey
– jersey
shorts
– pantalones cortos
a jumper
– jersey
a skirt
– falda
a shirt
– camisa
a suit
– traje
a sweater
– jersey
a tracksuit
– chándal
a sweatshirt
– sudadera
trousers
– pantalones
a T-shirt
– camiseta
a uniform
– uniforme
a waistcoat
– chaleco
Sleepwear (ropa de dormir)
English
Underwear (ropa interior)
Castellano
English
Castellano
a dressing gown
– bata
a bra
– sujetador
a nightgown
– camisón
knickers
– bragas
a pyjama
– pijama
pants
– calzoncillos
slippers
– zapatillas
socks
– calcetines
tights
– medias
Accessories (accesorios)
English
Castellano
English
Castellano
a bag
– bolso
a belt
– cinto
a bikini
– bikini
a bracelet
– pulsera
braces
– tirantes
a cap
– visera, gorra
earrings
– pendientes
glasses
– gafas
gloves
– guantes
a hat
– sombrero
a necklace
– collar
a scarf
– bufanda, fular
a swimming costume
– traje de baño
a tie
– corbata
Página 37 de 46
Wear: llevar puesto.
– I wear glasses (uso, llevo gafas).
– I'm wearing a skirt now (llevo una falda ahora).
Carry: llevar.
– I'm carrying a bag (llevo un bolso).
Fíjese en que:
Empleamos a (y no an) delante de "uniform".
Hay algunas piezas de ropa que son plurales: trousers, jeans, shorts, knickers, pants,
tights, el calzado...
– I'm wearing a T-shirt (llevo una camiseta).
– I'm wearing green trousers. I'm wearing a green trousers.
2.10.1 La expresión del tiempo
The days of the week (los días de la semana)
English
Castellano
English
Castellano
Monday
– lunes
Tuesday
– martes
Wednesday
– miércoles
Thursday
– jueves
Friday
– viernes
Saturday
– sábado
Sunday
– domingo
the weekend
– el fin de semana
The months of the year (los meses del año)
English
Castellano
English
Castellano
January
– enero
February
– febrero
March
– marzo
April
– abril
May
– mayo
June
– junio
July
– julio
August
– agosto
September
– septiembre
October
– octubre
November
– noviembre
December
– diciembre
The seasons of the year (las estaciones del año)
English
Castellano
English
Castellano
winter
– invierno
spring
– primavera
summer
– verano
autumn / fall
– otoño
Recuerde que los días de la semana y los meses del año se escriben con mayúscula.
Página 38 de 46
2.11 Soluciones de las actividades
S1.
1. Is Shakira - Yes, she is
2. Shakira isn't
3. Ricky Martin and Gerard Piqué are
4. Are Twilight and True Blood – they aren’t
5. Are you – Yes, I am / No, I’m not
6. Are you – Yes, I am / No, I’m not
7. I’m not
8. My favourite books are / aren’t
S2.
1. We are Melanie and Antonio and this is our bedroom.
– a) We have got / we’ve got a big wardrobe but we haven’t got any curtains.
–
b) Have you got a carpet? Yes, we have.
2. He is Jamie Oliver, the famous English cook and this is his kitchen.
– a) He has got / He’s got a white fridge but he hasn’t got a dishwasher.
–
b) Has he got a microwave? Yes, he has.
3. They are Lewis Hamilton, the famous F1 pilot, and his girlfriend. This is
their bathroom.
– a) They have got / they’ve got a bath but they haven’t got a blue washbasin.
–
b) Have they got a mirror? Yes, they have.
S3.
1. Are there two banks in the city? No, there aren’t.
2. There is / there’s a lake in the park.
3. There isn’t a sports centre opposite the church.
4. Is there a chemist's in the city? Yes, there is.
5. There aren’t two bridges in the park, there is / there’s only one.
6. There aren’t four trees in the park.
S4.
1. wakes up
6. has breakfast
2. doesn’t get up
7. drives to work
3. has a shower
8. starts work
4. has a bath
9. has lunch
5. gets dressed
10. finishes work
Página 39 de 46
11. does the shopping
16. listens to music
12. gets home
17. goes to sleep
13. cooks dinner
18. reads a book
14. has dinner
19. goes to the cinema
15. watches TV
20. goes for a drink
S5.
1. He plays volleyball but he doesn't go fishing.
2. We go swimming / we swim but we don’t do karate / we don’t do judo.
3. They go jogging but they don’t play the guitar.
4. She phones her friends / her family but she doesn’t go shopping.
S6.
1. Do Paul and Bill have a coffee? Yes, they do.
2. Do you cook? No, I don’t. I go sailing.
3. Does Ernest play hockey? No, he doesn’t. He goes waterskiing.
S7.
1. Do you cook eggs in the microwave? Yes, I do.
2. Are there ten shopping centres in your city? No, there aren’t.
3. Has Anna got any hobbies? Yes, she has.
4. I don’t go to school in the evening.
5. Is Nicolas Sarkozy French? Yes, he is.
6. My grandmother doesn’t watch TV every day.
7. My cat sleeps twenty hours a day.
8. My neighbours have got two new cars. They’re really expensive.
9. People from China speak Chinese.
10. Andrew and I work in an office.
S8.
1. They’re Steve Urkel’s braces.
2. They’re Letizia’s shoes.
3. It’s Lady Gaga’s dress.
4. It’s Michael Jackson’s jacket.
S9.
1. What is this? It’s an armchair.
2. What is that? It’s a shelf.
Página 40 de 46
3. What are these? They’re washing machines.
4. What are those? They’re blinds.
S10.
1. Kate isn’t wearing jeans.
2. Kate is holding Jack's hand.
3. Jack and Sawyer are wearing trousers.
4. Jack and Sawyer aren’t running.
5. I’m wearing / I’m not wearing a white T-shirt.
6. I’m sitting / I’m not sitting in a chair.
S11.
1. Is she swimming? Yes, she is.
2. Is he having a shower? No, he isn’t.
3. Is he doing the shopping? Yes, he is.
4. Is she doing yoga? No, she isn’t.
5. Are they thinking about each other? Yes, they are.
6. Is he getting dressed? Yes, he is.
S12.
Hábitos. Acciones
Presente
regulares
Verbos estáticos
Acciones que
ocurren ahora
nuo
– 4. It often rains in December.
– 5. My brother goes to the gym twice a week.
simple
Presente conti-
– 2. What do you usually do at the weekend?
Acciones tempora-
les
Planes futuros
– 8. Do you know that girl? Yes, but I don't remember her name.
– 10. Do you hate doing your homework?
– 1. Please be quiet! This is a library and people are studying.
– 3. What is he doing at the moment? He's making dinner.
– 7. They're redecorating their house this week.
– 6. I'm going to my aunt's house this weekend.
– 9. Mike's having a party tomorrow.
S13.
Presente simple
Presente continuo
every year
twice a month
never
once a week
on Sundays
twice a day
every morning
rarely
at the moment
today
right now
tomorrow
this month
Página 41 de 46
S14.
1. Julia isn't at home at the moment. She's visiting some friends.
2. What time do you usually have breakfast?
3. How often do the Simpsons go on holiday?
4. Rafael Nadal is a tennis player. He plays every day.
5. Why are you under the table? What are you doing?
6. Martin doesn't like tea. He prefers coffee.
S15.
1. my sister doesn’t usually go - she’s driving to work
2. I don’t know
3. I live - I’m living - I want
4. is he taking
5. does Mary usually do - she sometimes goes
6. it’s raining
7. she doesn’t play
8. the sun is shining - birds are singing
S16.
1. what
6. what time / when
2. who
7. why
3. when
8. how much
4. how many
9. what kind of
5. where
10. how often
S17.
Wh-questions with present simple
Pronombre interrogativo
…?
Verbo en forma interrogativa
Wh-word
Am / is / are
Sujeto
...?
2. Where
are
you
from?
6. Whose
is
this house?
Wh-word
have / has
Sujeto
got
5. How many pets
has
your son
got?
...?
Wh-word
is / are
there
...?
4. How many students
are
there
in your class?
Wh-word
do / does
Sujeto
Infinitivo
...?
1. How often
does
your brother
go
to the gym?
3. Why
do
you
like
Cristiano Ronaldo?
Página 42 de 46
S18.
To be.
– 1. Who are Steve and Jack?
–
2. What is his name?
Have got.
– 3. How many doors has your car got?
–
4. What have you got in your bedroom?
–
5. Where has she got her keys?
There is/are.
– 6. How many students are there in this class?
–
7. Where is there a hospital in this town?
Other verbs.
– 8. What time do the banks close in England?
–
9. How often does he go swimming?
–
10. Why do you smoke?
S19.
1. What time does he get up?
2. How often does he have a shower?
3. Who makes breakfast?
4. Where does he watch TV?
5. How does his mother go to work?
6. Why does he love cats?
S20.
1. Why are the children on holiday?
2. Where is James?
3. Where have you got your Britney’s CD?
4. How much milk have they got in their fridge?
5. How many students are there in class?
6. What time / when do you have lunch?
7. Why does she do yoga?
8. Who do you love?
Página 43 de 46
S21.
Wh-questions with present continuous
Pronombre interrogativo
…?
Verbo en forma interrogativa
Wh-word
is / am / are
Sujeto
-ing?
...?
1. What
is
your sister
listening
to?
2. Where
are
you
going
to?
3. Why
are
you
wearing
a coat?
S22.
1. When is she doing
karate?
3. Where are you having breakfast?
2. Why are you watching
TV?
5. What are you reading?
4. How is Peter driving?
S23.
a. It’s twenty past four.
d. It’s (a) quarter to eleven.
b. It’s three o’clock.
y. It’s half past eight.
c. It’s ten to nine.
f. It’s twenty-five to twelve.
S24.
1c – 2f – 3d – 4e – 5a – 6b – 7g
Dates
We say
We write
1. 14 February
The fourteenth of February
2. 17 March
The seventeenth of March
3. 1 April
The first of April
4. 4 July
The fourth of July
5. 31 October
The thirty-first of October
6. 5 November
The fifth of November
7. 25 December
The twenty-fifth of December
Página 44 de 46
Event
Valentine’s Day
St Patrick’s Day
April Fool’s Day
Independence Day
Halloween
Bonfire Night
Christmas
S25.
1. at
6. 11. on
2. on
7. at
12. in
3. at
8. on
13. at
4. on
9. 14. on
5. in
10. in
S26.
1. True.
2. False. Saint Patrick’s Day is celebrated in Ireland but also in many other
English-speaking countries like the USA and Australia.
3. False. Saint Patrick is from Scotland.
4. False. Saint Patrick died on 17th March.
5. True.
6. You can find a green river in Chicago.
S27.
1. I don’t understand.
4. Molly usually empties
2. is she doing–she’s sitting
5. does your brother do
3. I’m meeting–do you want
S28.
1. How many dishes are there in the sink?
2. What time / when does she get up?
3. Why is she wearing a coat?
4. Where has she got a mirror?
5. How often do you go to work?
S29.
1. Monday, the third of January
2. Wednesday, the thirty-first of September
3. Saturday, the twelfth of October
4. Sunday, the fifth of May
5. Friday, the twenty-second of August
S30.
1. on – at – in
5. on
2. - in – on
3. on – at
4. at
Página 45 de 46
S31.
1a – 2c – 3c – 4b – 5a
Página 46 de 46