Diapos
Anuncio
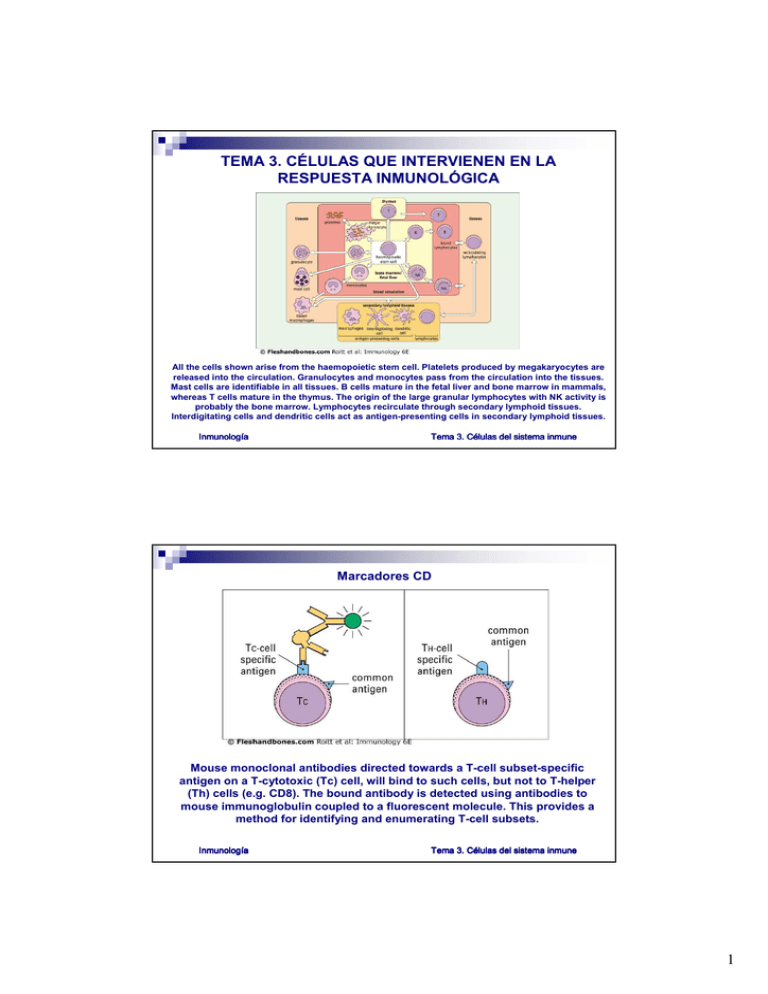
TEMA 3. CÉLULAS QUE INTERVIENEN EN LA RESPUESTA INMUNOLÓGICA All the cells shown arise from the haemopoietic stem cell. Platelets produced by megakaryocytes are released into the circulation. Granulocytes and monocytes pass from the circulation into the tissues. Mast cells are identifiable in all tissues. B cells mature in the fetal liver and bone marrow in mammals, whereas T cells mature in the thymus. The origin of the large granular lymphocytes with NK activity is probably the bone marrow. Lymphocytes recirculate through secondary lymphoid tissues. Interdigitating cells and dendritic cells act as antigen-presenting cells in secondary lymphoid tissues. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 3. Cé Células del sistema inmune Marcadores CD Mouse monoclonal antibodies directed towards a T-cell subset-specific antigen on a T-cytotoxic (Tc) cell, will bind to such cells, but not to T-helper (Th) cells (e.g. CD8). The bound antibody is detected using antibodies to mouse immunoglobulin coupled to a fluorescent molecule. This provides a method for identifying and enumerating T-cell subsets. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 3. Cé Células del sistema inmune 1 Los linfocitos T cells express either γδ or αβ TCR. T cells are divided into CD4 and CD8 subsets which determine whether they see antigen (peptides) with MHC class II or I, respectively. CD4+ T cells can be further subdivided into Th1 and Th2 on the basis of their cytokine profiles. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 3. Cé Células del sistema inmune El sistema fagocítico mononuclear Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 3. Cé Células del sistema inmune 2 Descriptions of the Fc receptors can be found in 4.22 and 4.23. ss = subset, a = activated, b = basophils, e = eosinophils Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 3. Cé Células del sistema inmune Las células presentadoras de antígeno Bone-marrow-derived antigen-presenting cells (APCs) are found especially in lymphoid tissues, in the skin and in mucosa. APCs in the form of Langerhans' cells are found in the epidermis and are characterized by special granules (the tennis-racquet-shaped Birbeck granules). These cells, rich in MHC class II, carry processed antigens and migrate via the afferent lymphatics (where they appear as 'veiled' cells) into the paracortex of the draining lymph nodes. Here they make contact with T cells. These 'interdigitating cells', localized in the T-celldependent cells areas of the lymph node, present antigen to T-helper cells. Exposure of antigen to B cells occurs on the follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) in the germinal centres of B-cell follicles. Some macrophages located in the outer cortex and marginal sinus may also act as APCs. In the thymus, APCs occur as interdigitating cells in the medulla. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 3. Cé Células del sistema inmune 3 Langerhans' cells (LC), interdigitating dendritic cells (IDC), germinal centre dendritic cells (GCDC) and B cells are rich in MHC class II for communicating with CD4+ T cells. CD4 expressed by only some APCs may allow their infection with HIV. Macrophages (M) possess low levels of MHC class II for antigen presentation and are mainly phagocytic cells. Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) located within the primary and secondary follicles do not express class II MHC, but have high levels of FcγR, CR1 and CR2 to enable them to trap immune complexes (iccosomes) for presentation to B cells. NSE = non-specific esterase. Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 3. Cé Células del sistema inmune Inmunologí Inmunología Tema 3. Cé Células del sistema inmune 4