LOS VERBOS MODALES
Anuncio
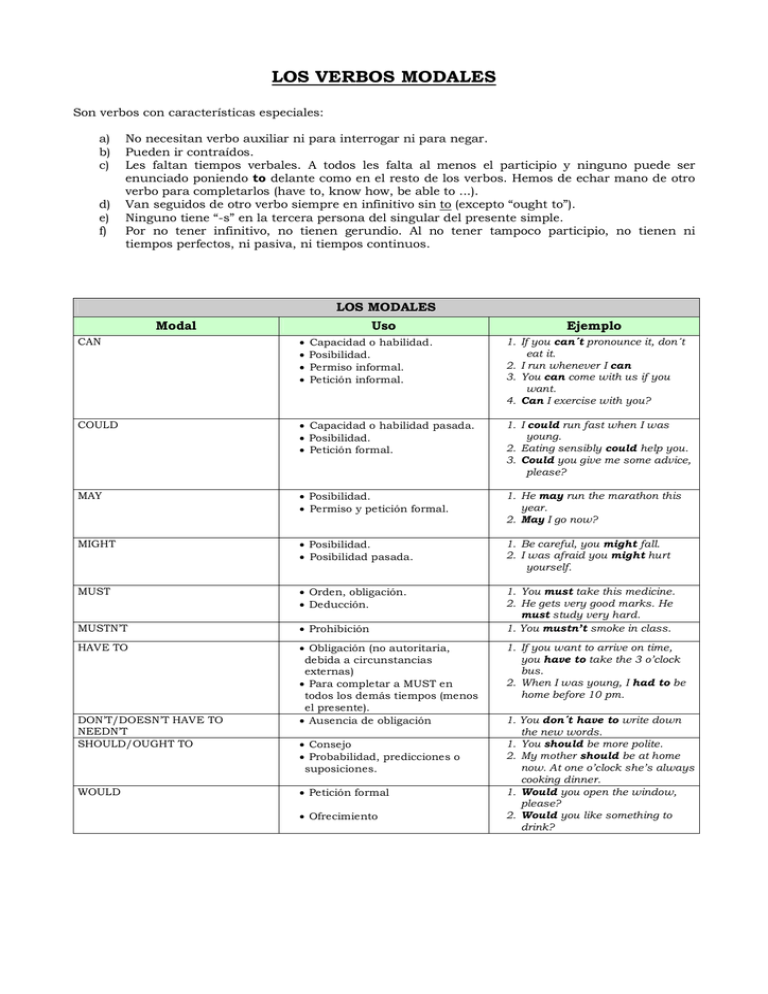
LOS VERBOS MODALES Son verbos con características especiales: a) b) c) d) e) f) No necesitan verbo auxiliar ni para interrogar ni para negar. Pueden ir contraídos. Les faltan tiempos verbales. A todos les falta al menos el participio y ninguno puede ser enunciado poniendo to delante como en el resto de los verbos. Hemos de echar mano de otro verbo para completarlos (have to, know how, be able to ...). Van seguidos de otro verbo siempre en infinitivo sin to (excepto “ought to”). Ninguno tiene “-s” en la tercera persona del singular del presente simple. Por no tener infinitivo, no tienen gerundio. Al no tener tampoco participio, no tienen ni tiempos perfectos, ni pasiva, ni tiempos continuos. LOS MODALES Modal Uso Ejemplo CAN COULD Capacidad o habilidad pasada. Posibilidad. Petición formal. 1. I could run fast when I was young. 2. Eating sensibly could help you. 3. Could you give me some advice, please? MAY Posibilidad. Permiso y petición formal. 1. He may run the marathon this year. 2. May I go now? MIGHT Posibilidad. Posibilidad pasada. 1. Be careful, you might fall. 2. I was afraid you might hurt yourself. MUST Orden, obligación. Deducción. MUSTN’T Prohibición 1. You must take this medicine. 2. He gets very good marks. He must study very hard. 1. You mustn’t smoke in class. HAVE TO Obligación (no autoritaria, debida a circunstancias externas) Para completar a MUST en todos los demás tiempos (menos el presente). Ausencia de obligación DON’T/DOESN’T HAVE TO NEEDN’T SHOULD/OUGHT TO WOULD Capacidad o habilidad. Posibilidad. Permiso informal. Petición informal. Consejo Probabilidad, predicciones o suposiciones. Petición formal Ofrecimiento 1. If you can´t pronounce it, don´t eat it. 2. I run whenever I can 3. You can come with us if you want. 4. Can I exercise with you? 1. If you want to arrive on time, you have to take the 3 o’clock bus. 2. When I was young, I had to be home before 10 pm. 1. You don´t have to write down the new words. 1. You should be more polite. 2. My mother should be at home now. At one o’clock she’s always cooking dinner. 1. Would you open the window, please? 2. Would you like something to drink? LOS MODALES PERFECTOS Modal Uso Ejemplo COULD HAVE Habilidad para haber hecho algo It was a stupid thing to do. You could have hurt yourself. que no se hizo. COULDN’T HAVE Seguridad de que algo no ocurrió Suposición sobre un hecho pasado Seguridad o conclusión lógica sobre un suceso pasado Queja sobre algo que ocurrió / lamento de que no se haya cumplido algo que se esperaba Opinión crítica sobre un hecho pasado, indicando que no debería haber ocurrido Deseo de haber hecho algo que no se hizo por factores o circunstancias externas MAY / MIGHT HAVE MUST HAVE SHOULD / OUGHT TO HAVE SHOULDN’T HAVE WOULD HAVE Eric couldn’t have broken the vase. He wasn’t at home. Elisa may/might have taken the wrong bus I hear you’ve been to Scotland. That must have been interesting. You should/ought to have warned me earlier. I shouldn’t have eaten so much. I would have gone to the party, but I was too busy.



