LA CÉLULA
Anuncio

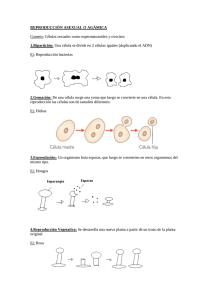
LA CÉLULA LA CÉLULA ES CONSIDERADA COMO LA UNIDAD FUNDAMENTAL TANTO ESTRUCTURAL COMO DE FUNCIONAMIENTO EN LOS SERES VIVOS. ES DECIR, LA CÉLULA ES LA MÍNIMA PARTE EN QUE SE PUEDE DIVIDIR A UN ORGANISMO Y ES LA ENTIDAD MÁS PEQUEÑA QUE REÚNE EL CONJUNTO DE PROPIEDADES QUE SE PUEDEN ASOCIAR CON LA MATERIA VIVIENTE. PARTES FUNDAMENTALES DE LA CÉLULA PARTES FUNDAMENTALES DE LA CÉLULA NÚCLEO MEMBRANA CELULAR ES EL CENTRO DE CONTROL Y COORDINACIÓN DE LOS PROCESOS VITALES, COMO LA NUTRICIÓN, LA REPRODUCCIÓN Y EL CRECIMIENTO DE LA CÉLULA. ES UNA CAPA FINA QUE ENVUELVE A LA CÉLULA. SU FUNCIÓN ES PROTEGERLA, SELECCIONAR LOS NUTRIENTES QUE DEBEN ENTRAR, Y PERMITIR LA SALIDA DE LOS DESECHOS. CITOPLASMA SE ENCUENTRA EN EL INTERIOR DE LA CÉLULA Y ES TRANSPARENTE. SU CONSISTENCIA SE PARECE A LA DE LA GELATINA BLANDA. ELLA CONTIENE LOS ORGANELOS. ORGANELOS CITOPLASMÁTICOS PEQUEÑOS CUERPOS ENCARGADOS DE REALIZAR LAS DIFERENTES FUNCIONES VITALES DE LA CÉLULA. CLASES DE CÉLULAS CELULA ANIMAL CELULA VEGETAL FUNCIONES DE LOS ORGANELOS EN LA CÉLULA Los organelos se encargan de realizar una función específica en la célula. (Los que se encuentran en color verde son exclusivos de la célula animal) Mitocondrias: Realizan la respiración celular, necesitan la entrada de oxígeno para producir energía. Aparato de Golgi: Expulsa sustancias de desecho fuera de la célula. Retículo Endoplasmático: Almacena proteínas y las transporta tanto al interior como hacia el exterior de la célula. Lisosomas: Llevan a cabo la función digestiva, al transformar los alimentos en sustancias más sencillas. Ribosomas: Producen proteínas. Cloroplastos: Contiene la clorofila y en ellos se produce la fotosíntesis. Vacuola: Almacena sustancias de reserva. Puede haber una o mas y es generalmente más grande que los demás organelos. EL TAMAÑO Y LA FORMA DE LAS CÉLULAS Casi todas las células son tan pequeñas que no se ven a simple vista. Un ejemplo de célula macroscópica (la puedes identificar a simple vista) es: En un centímetro caben aproximadamente unas mil células, puestas en fila. Al observar las células con un microscopio, se puede comprobar que tienen formas variadas: Alargadas. Disco. Estrella. Planas. Flagelo. Poligonal. CELULAS ALGARGADAS Las células de los músculos son alargadas. CÉLULAS EN FORMA DE DISCO Los glóbulos rojos son células en forma de disco. CÉLULAS EN FORMA DE ESTRELLA Las células nerviosas tienen forma de estrella. CÉLULAS PLANAS Las células superficiales de la piel son planas. CÉLULAS EN FORMA DE FLAGELO Las células reproductoras masculinas, los espermatozoides, tienen un flagelo, con el que se desplazan. CÉLULAS EN FORMA POLIGONAL Las células vegetales suelen tener forma poligonal. Debido a su rigidez de la pared celular, las células encajan como los ladrillos de un muro. ACTIVIDAD EN CLASE Escribe en tu cuaderno: 1. Dirige todas las actividades de la célula. 2. Líquido viscoso que contiene los organelos. 3. Envoltura externa de la célula. 4. Componentes que realizan diferentes funciones. ORGANISMOS UNICELULARES Y PLURICELULARES LOS SERES VIVOS PUEDEN CLASIFICARSE EN UNICELULARES Y PLURICELULARES. SERES VIVOS UNICELULARES ESTÁN FORMADOS POR UNA SOLA CÉLULA. PUEDEN VIVIR INDEPENDIENTEMENTE Y CONSTITUYEN POR SI MISMO UN ORGANISMOS, COMO POR EJEMPLO: EL PARAMECIO Y LA AMEBA. AMEBA Y PARAMECIO SERES VIVOS PLURICELULARES ESTÁN FORMADOS POR MUCHAS CÉLULAS. EN LOS ORGANISMOS PLURICELULARES CADA CÉLULA PARTICIPA ESPECIFICAMENTE EN UNA TAREA. EJEMPLO: ANIMALES, PLANTAS Y HONGOS ANIMALES PLANTAS HONGO